Key points
- Initial symptoms of yellow fever can include fever, chills, severe headache, back pain, general body aches, nausea, vomiting, fatigue (feeling tired), and weakness.
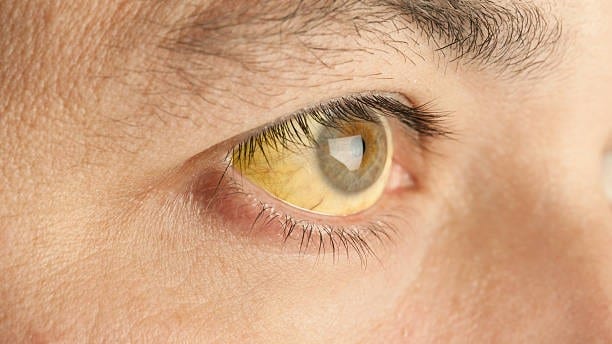
- Severe symptoms include high fever, yellow skin or eyes (jaundice), bleeding, shock, and organ failure.
- If you think you or a family member might have yellow fever, talk with your healthcare provider.
- Vaccination is recommended for travelers going to yellow fever risk areas.
- There is no specific treatment for yellow fever.
Symptoms
Most people infected with yellow fever virus will either have no symptoms or mild symptoms and completely recover. For people who develop symptoms, the time from infection until illness is typically 3 to 6 days.
- Initial symptoms can include sudden onset of fever, chills, severe headache, back pain, general body aches, nausea, vomiting, fatigue (feeling tired), and weakness.
- Most people who develop symptoms improve within one week.
- For some people who recover, weakness and fatigue (feeling tired) might last several months.
- Most people who develop symptoms improve within one week.
- A few people will develop a more severe form of the disease.
- For 1 out of 7 people who have the initial symptoms, there will be a brief remission (a time you feel better) that may last only a few hours or for a day, followed by symptoms of more severe disease.
- Severe symptoms include high fever, yellow skin or eyes (jaundice), bleeding, shock, and organ failure.
- Among those who develop severe disease, 30-60% die.
- For 1 out of 7 people who have the initial symptoms, there will be a brief remission (a time you feel better) that may last only a few hours or for a day, followed by symptoms of more severe disease.
- Once you have been infected, you are likely protected against future infections.
Diagnosis
See your healthcare provider if you have visited an area where yellow fever is found and have symptoms described above.
- Tell your healthcare provider when and where you traveled.
- Your healthcare provider can order blood tests to look for yellow fever or other similar viruses, like dengue.
More information on diagnostic testing is available on the For Healthcare Providers page.
Treatment
- There is no medicine to treat yellow fever. However, a vaccine is available to prevent disease.
- Rest, drink fluids, and use over-the-counter pain relievers to reduce fever and relieve aching.
- Avoid certain medications, such as aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve), which may increase the risk of bleeding.
- Avoid certain medications, such as aspirin or other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or naproxen (Aleve), which may increase the risk of bleeding.
- People with severe symptoms of yellow fever infection should be hospitalized for close observation and supportive care.
- If after returning from travel you have symptoms of yellow fever, protect yourself from mosquito bites for up to 5 days after symptoms begin. This will help prevent spreading yellow fever virus to uninfected mosquitoes that can spread the virus to other people.
