Key points
- 1 in 4: About one in four people infected with dengue will get sick.
- For people who get sick with dengue, symptoms can be mild or severe.
- Severe dengue can be life-threatening within a few hours and often requires care at a hospital.

Symptoms
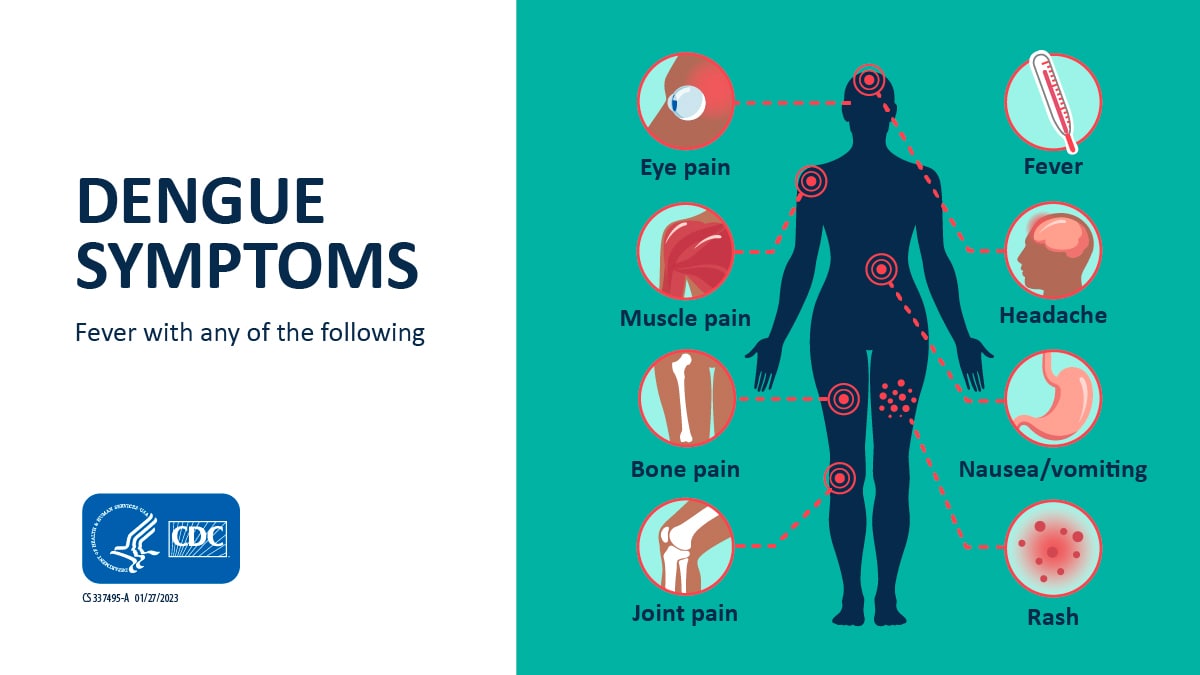
The most common symptom of dengue is fever with any of the following:
- Aches and pains (eye pain, typically behind the eyes, muscle, joint, or bone pain)
- Nausea, vomiting
- Rash
- Any warning sign
- Mild symptoms of dengue can be confused with other illnesses that cause fever.
- Symptoms of dengue typically last 2–7 days.
- Most people will recover after about a week.
When to seek emergency help
Symptoms of dengue can become severe within a few hours. Severe dengue is a medical emergency.
About 1 in 20 people who get sick with dengue will develop severe dengue. Severe dengue can result in shock, internal bleeding, and death.
Immediately go to a local clinic or emergency room if you or a family member has any of the following symptoms:
- Belly pain or tenderness
- Vomiting (at least 3 times in 24 hours)
- Bleeding from the nose or gums
- Vomiting blood, or blood in the stool
- Feeling extremely tired or restless
Warning Signs
Testing
- See your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of dengue and live in or have recently traveled to an area with risk of dengue.
- A blood test is the only way to confirm the diagnosis.
- Laboratory confirmation is not required to manage illness from dengue, and your healthcare provider might provide care based on your signs and symptoms.
- Laboratory confirmation is not required to manage illness from dengue, and your healthcare provider might provide care based on your signs and symptoms.
- Your healthcare provider may order blood tests to look for dengue or other similar viruses like Zika or chikungunya.
