At a glance
Tuberculosis (TB) disease is a nationally notifiable disease, and reporting is mandated in all U.S. states.

Overview
Case reporting for TB disease
Tuberculosis has been a nationally notifiable disease since 1951. Today, CDC collects information about cases of TB disease electronically. TB disease case reporting is essential to help control and eventually eliminate TB disease in the United States.
CDC uses these data to:
- Identify outbreaks of TB disease
- Track best practices in treating TB disease
- Monitor TB outcomes
- Inform TB prevention and intervention guidance and policy
- Monitor progress towards TB elimination in the United States
State and local TB programs use these data to inform TB activities at the local level. CDC also makes these data available to internal and external research partners to pursue research projects that add to the scientific and clinical understanding of TB in the United States.
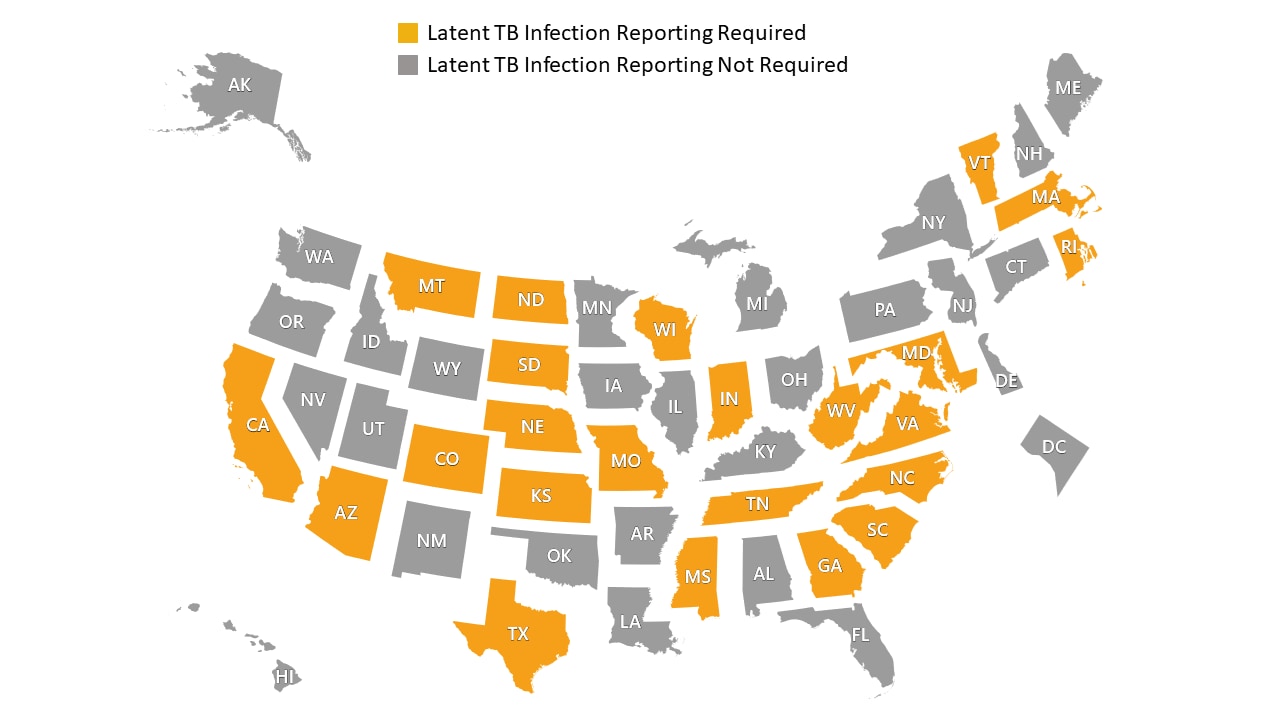
Case reporting for latent TB infection
Reporting cases of latent TB infection to CDC is optional. Some states and localities have developed legal reporting requirements for latent TB infection to track progress towards TB elimination, facilitate notification to state TB programs, and help local health departments treat latent TB infection to prevent TB disease. Contact your state or local TB program for the reporting requirements for your jurisdiction.
Other reporting requirements
Civil surgeons and panel physicians may have additional reporting requirements. Refer to the technical instructions for more information:
- Technical Instructions for Panel Physicians: Tuberculosis
- Technical Instructions for Civil Surgeons: Tuberculosis