Key points
- Streptococcus pneumoniae can cause many different types of infections.
- Symptoms depend on the part of the body that's infected.
- Serious infections can result in long-term health problems or death.
- Complications aren't common for mild infections.

Symptoms
It usually takes 1 to 3 days for pneumonia symptoms to appear after S. pneumoniae bacteria enter someone's body. Experts don't know how long it takes for symptoms to appear for other types of pneumococcal disease.
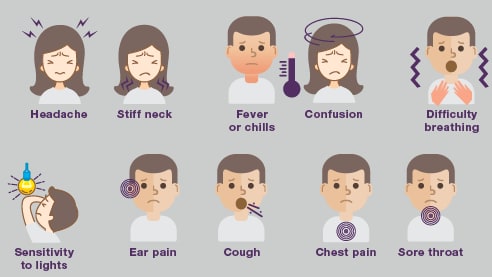
Symptoms of pneumococcal disease depend on the part of the body that's infected. Generally, the symptoms are similar to other bacterial infections in that part of the body.
Serious infections
Pneumonia
Symptoms of pneumococcal pneumonia, a lung infection, include:
- Chest pain
- Cough
- Fever and chills
- Rapid breathing or difficulty breathing
Older adults may experience confusion or low alertness, rather than the more common symptoms listed above.
Meningitis
Symptoms of pneumococcal meningitis, an infection of the lining of the brain and spinal cord, include:
- Confusion
- Fever
- Headache
- Photophobia (eyes being more sensitive to light)
- Stiff neck
In babies, meningitis may cause poor eating and drinking, low alertness, and vomiting.
Bacteremia (bloodstream infection)
Symptoms of pneumococcal bacteremia, a bloodstream infection, include:
- Chills
- Fever
- Low alertness
Mild infections
Ear infection
Symptoms of ear infections include:
- A red, swollen ear drum
- Ear pain
- Fever
- Sleepiness
Sinus infection
Symptoms of sinus infections include:
- Bad breath
- Cough
- Facial pain or pressure
- Headache
- Post-nasal drip (mucus dripping down the throat)
- Runny or stuffy nose
- Sore throat
Complications
When to seek medical care
Serious infections can result in sepsis, long-term problems, or death. Sepsis is a life-threatening emergency resulting from the body's extreme response to infection.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia can cause:
- Airway blockage, collapsed lungs, and lung abscesses (pus)
- Empyema (infection around the lungs and in the chest cavity)
- Pericarditis (inflammation of the outer lining of the heart)
Pneumococcal pneumonia kills about 1 in 20 people who get it.
Meningitis
Meningitis can cause developmental delay or hearing loss.
About 1 in 12 children and 1 in 6 older adults who get pneumococcal meningitis dies of the infection.
Bacteremia
Bacteremia can result in loss of limbs.
About 1 in 30 children with pneumococcal bacteremia die of it. Pneumococcal bacteremia kills about 1 in 8 adults who get it.
Minor infections
Complications are rare and not usually severe for mild infections like ear and sinus infections.
