Key points
- Mumps is best known for causing puffy cheeks and a tender, swollen jaw.
- Mumps is usually mild, but in rare cases it can cause more severe complications like brain inflammation.
- Most people show symptoms 2 to 4 weeks after infection and recover within 2 weeks.
Early symptoms
Mumps is a contagious disease caused by a virus that infects the salivary glands. Symptoms that might begin a few days before jaw swelling include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Tiredness
- Loss of appetite
Common symptoms
Mumps is best known for causing puffy cheeks and a tender, swollen jaw. This swelling of the parotid salivary glands under the ears on one or both sides is called parotitis.

Symptoms typically appear 16 to 18 days after infection, but they may appear 12 to 25 days after infection.
Some people with mumps have very mild symptoms (like a cold). Some people have no symptoms at all and may not know they have mumps. In rare cases, mumps can cause more severe complications.
Most people with mumps recover completely within 2 weeks.
Complications
In most people, mumps is pretty mild. In rare cases, mumps is deadly can cause more severe complications.
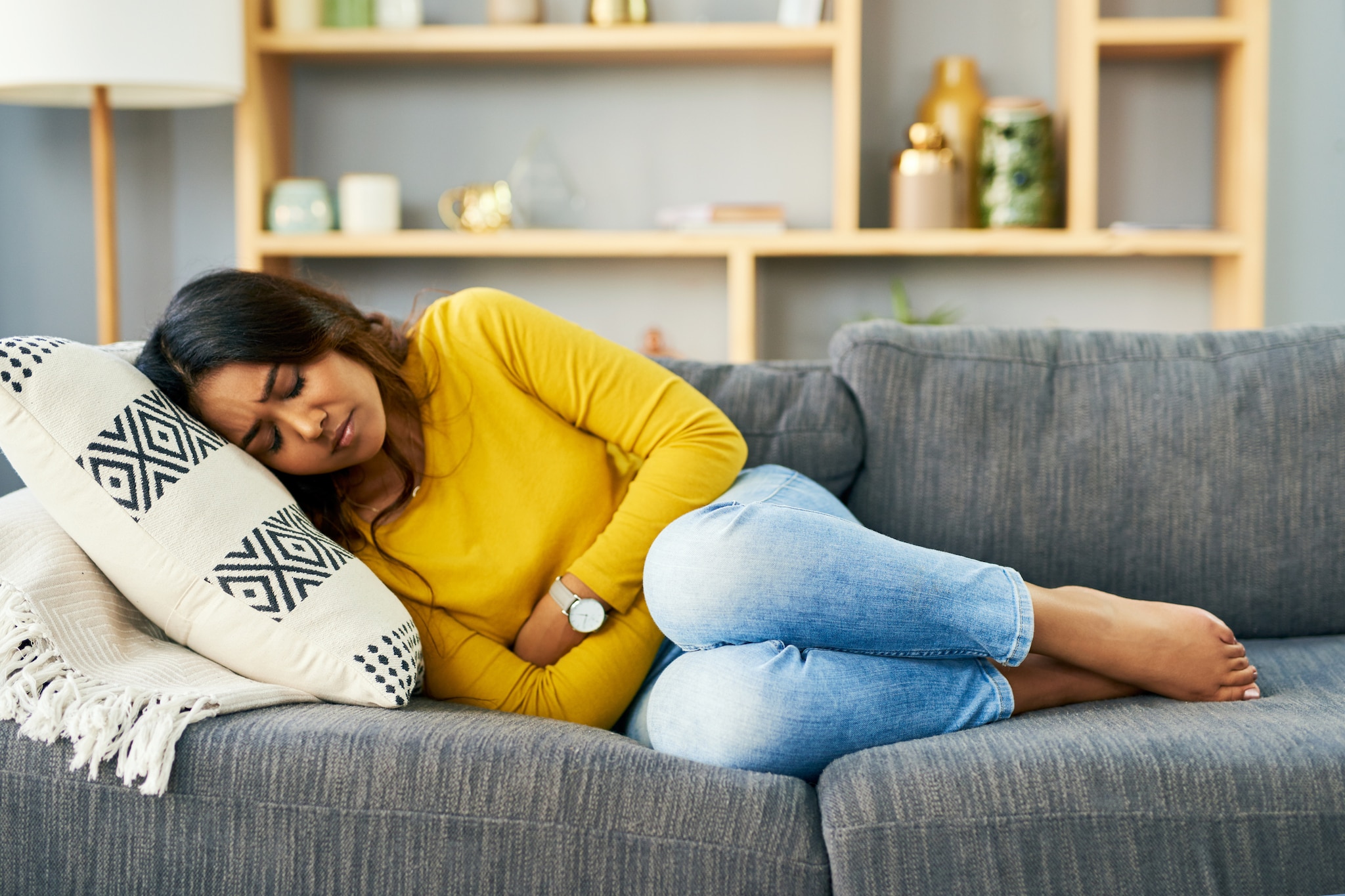

Complications can include:
- Inflammation of the testicles (orchitis); this may lead to a decrease in testicular size (testicular atrophy)
- Inflammation of the ovaries (oophoritis) and/or breast tissue (mastitis)
- Inflammation in the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- Inflammation of the brain (encephalitis); they can lead to death or permanent disability
- Inflammation of the tissue covering the brain and spinal cord (meningitis)
- Loss of hearing (temporary or permanent)
Inflammation of the testicles could lead to temporary sterility or decrease fertility in men; but no studies have assessed if it results in permanent infertility.
