Key points
- Serologic testing is the primary method for diagnosing Jamestown Canyon virus disease.
- A positive Jamestown Canyon virus-specific immunoglobulin (Ig) M test result should be confirmed by neutralizing antibody testing at a state public health laboratory or CDC.
- Contact your state or local health department for assistance with diagnostic testing.

Considerations
Serologic testing remains the primary method for diagnosing Jamestown Canyon virus disease. However, several studies have found a high prevalence of seropositivity for Jamestown Canyon virus in humans, suggesting a high proportion of asymptomatic infections. In addition, it is not known how long IgM antibodies can be detected in serum following a Jamestown Canyon virus infection; therefore, a positive IgM antibody test may reflect past infection. This can make interpreting serologic testing difficult when diagnosing a patient with acute disease.
For immunocompromised patients, molecular testing (e.g., RT-PCR) might be more sensitive than serologic testing.
Jamestown Canyon virus disease is a nationally notifiable condition. All cases should be reported to local public health authorities in a timely manner. Reporting can assist local, state, and national authorities to recognize outbreaks and to implement control measures to reduce further infections.
Recommended tests
Combined with a consistent clinical presentation, a preliminary diagnosis of Jamestown Canyon virus disease can be made by detection of Jamestown Canyon virus-specific IgM antibodies in serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- Jamestown Canyon virus-specific IgM testing can be done at some state public health laboratories and at CDC.
- Commercial IgM testing for California serogroup viruses is available and can be used for initial testing.
- A positive Jamestown Canyon virus or California serogroup virus IgM test result should be confirmed by neutralizing antibody testing at a state public health laboratory or CDC.
- Because of the high prevalence of Jamestown Canyon virus antibodies in asymptomatic persons, diagnosis of a recent Jamestown Canyon virus infection is most accurately made by testing acute and convalescent sera to assess for at least a 4-fold rise in neutralizing antibody titers. If a convalescent cannot be obtained, use epidemiological and clinicial information to determine the likelihood of an acute infection.
- Some patients who are severely immunocompromised might require molecular (e.g., RT-PCR) testing for diagnosis.
To submit specimens for testing, please contact your state or local health department. They can assist you with determining if samples should be sent to the CDC Arbovirus Diagnostic Laboratory for further testing. Specimens should be submitted to CDC through state health departments. All results will be sent from CDC to the appropriate state health department.
Diagnostic Algorithm
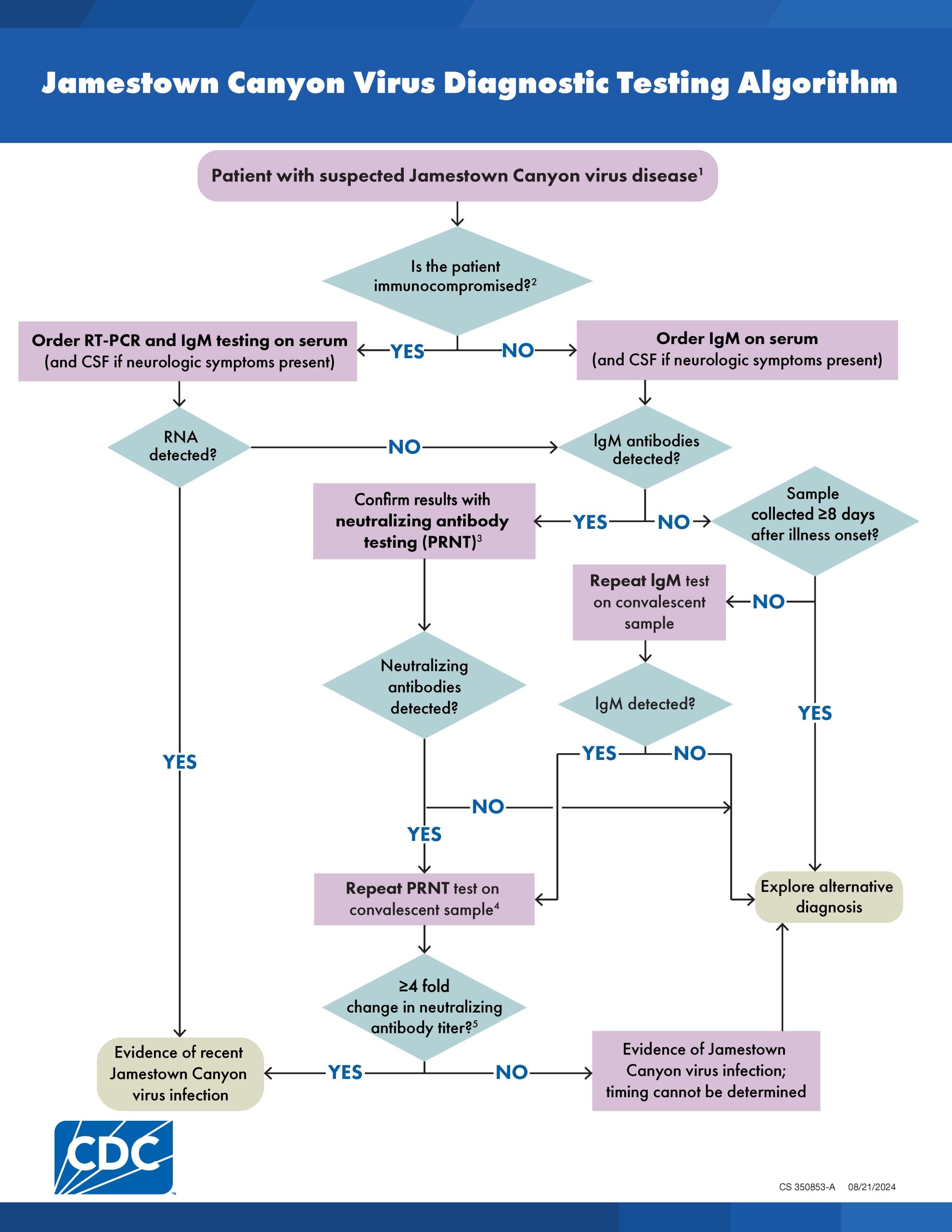
Jamestown Canyon Virus Diagnostic Algorithm
- Solomon IH, Ganesh VS, Yu G, Deng XD, Wilson MR, Miller S, et al. Fatal case of chronic Jamestown Canyon virus encephalitis diagnosed by metagenomic sequencing in patient receiving rituximab. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27(1):238–242. doi: 10.3201/eid2701.203448
- Grimstad PR, Shabino CL, Calisher CH, Waldman RJ. A case of encephalitis in a human associated with a serologic rise to Jamestown Canyon virus. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982;31(6):1238–1244. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.1238
- Grimstad PR, Calisher CH, Harroff RN, Wentworth BB. Jamestown Canyon virus (California serogroup) is the etiologic agent of widespread infection in Michigan humans. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986;35(2):376–386. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.376
- Kosoy O, Rabe I, Geissler A, Adjemian J, Panella A, Laven J, et al. Serological survey for antibodies to mosquito-borne bunyaviruses among US National Park Service and US Forest Service employees. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis, 2016;16(3):191–198. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2015.1865
- Huang C, Campbell W, Grady L, Kirouac I, LaForce FM. Diagnosis of Jamestown Canyon encephalitis by polymerase chain reaction. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28(6):1294–1297. doi: 10.1086/514789
