Key points
- CDC conducts active surveillance for invasive group B Streptococcus (group B strep, GBS) disease.
- Invasive disease refers to when bacteria invade parts of the body, like blood, that are normally free from germs.
- GBS bacteria remain a leading cause of meningitis and bloodstream infections in newborns younger than 3 months old.

Data systems
GBS disease is not reportable in most states.
Active Bacterial Core surveillance
CDC conducts active surveillance for invasive GBS disease through Active Bacterial Core surveillance (ABCs). ABCs is part of CDC's Emerging Infections Program.
Bact Facts Interactive
How the data are interpreted
GBS bacteria emerged in the 1970s as the most common cause of sepsis in newborns. More recently, experts recognized the increasing impact invasive GBS disease has on adults.
Disease burden
Approximately 28,010 cases of invasive GBS disease occur annually in the United States in all age groups.
GBS bacteria remain a leading cause of meningitis and bloodstream infections in newborns younger than 3 months old.
Disease trends
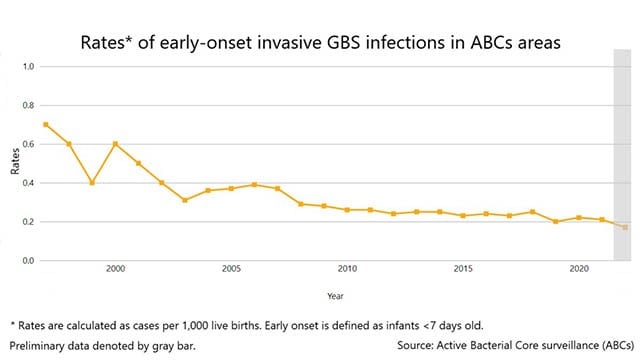
As use of intrapartum prophylaxis increased, GBS disease declined by 80% in babies younger than one week old:
- Infection rate in 1993: 1.7 cases per 1,000 live births
- Infection rate in 2020: 0.2 cases per 1,000 live births