Key points
- Lymphatic filariasis is caused by parasitic worms.
- These worms spread by mosquito bites.
- The worms attack the lymph system, causing fluid to build up in limbs.
Causes
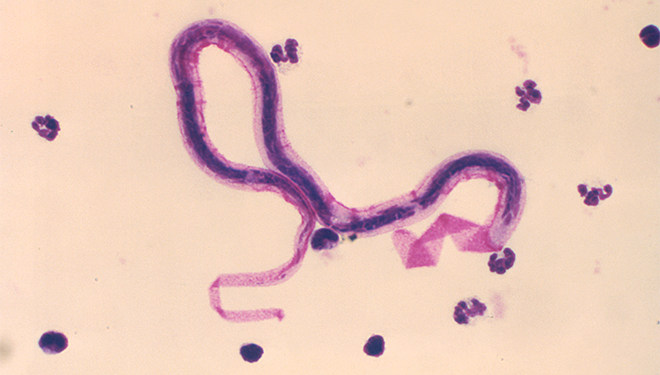
Lymphatic filariasis is caused by parasitic worms that are too small to be seen without a microscope. There are three species of the parasite that can cause this illness.
People get lymphatic filariasis when bitten by an infectious mosquito carrying the parasite. For the mosquito to become infectious, they must bite, or take a blood meal, from a person already infected with the parasite. About a week or so later, that same mosquito will bite the next person and the parasite may enter through the body through the person's skin. And the cycle of infection continues.
Once inside your body, the immature worms make their home in the person's lymphatic system. They can live for 5 – 7 years there, eventually damaging the lymphatic vessels.
