
Stool Specimens – Intestinal Parasites: Comparative Morphology Tables
Table 1: Characteristics of Intestinal Amebae Visible in Different Types of Fecal Preparations
| UNSTAINED | TEMPORARY STAINS | PERMANENT STAINS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Characteristic | Saline | Formalin | Iodine (Cysts) | Buffered Methylene Blue1 (Trophs) | |
| Trophozoites | Motility | + | ||||
| Cytoplasm | ||||||
| Appearance | + | + | + | + | ||
| Inclusions (rbc., bacteria) | + | + | + | + | ||
| Nucleus | +2 | + | + | |||
| Cysts | Nuclei | + | + | + | ||
| Chromatoid bodies | + | + | +3 | + | ||
| Glycogen | + | (vacuole present) | ||||
- Quensel’s stain may be substituted for buffered methylene blue.
- Nuclei of trophozoites are visible in formalin-fixed material but are usually not sufficiently distinctive for species identification.
- Chromatoid bodies are more easily seen in unstained wet mounts than in iodine preparations.
Table 2: Characteristics of Intestinal Flagellates, Ciliate, and Coccidia Visible in Different Types of Fecal Preparations
| UNSTAINED | TEMPORARY STAINS | PERMANENT STAINS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Characteristic | Saline | Formalin | Iodine (Cysts) | Neutral Red1 (Trophs) | |
| Trophozoites | Motility | + | | + | | |
| Shape | + | + | + | + (may be distorted) |
||
| Nucleus | | + | + | + | ||
| Flagella | ± | | + | ± | ||
| Other features2 | + | + | + | + | ||
| Cysts | Shape | + | + | + | + | |
| Nuclei | | + | + | + | ||
| Fibrils | ± | + | + | + | ||
| UNSTAINED | TEMPORARY STAINS | PERMANENT STAINS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage | Characteristic | Saline | Formalin | Iodine (Cysts) | Neutral Red1 (Trophs) | |
| Trophozoites | Motility | + | | + | | |
| Macronucleus | + | + | + | + | ||
| Cilia | + | + | + | + | ||
| Cysts | Macronucleus | + | + | ± | + | |
| UNSTAINED | TEMPORARY STAINS | PERMANENT STAINS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristic | Saline | Formalin | Iodine (Cysts) | Neutral Red1 (Trophs) | |
| Oocysts/Sporocysts | + | + | + | ±3 | |
- Neutral red dye in methocel solutions.
- The undulating membrane of Trichomonas and the spiral groove of Chilomastix may not be visible in all cases.
- Cryptosporidium oocysts can be demonstrated in acid-fast stains.
Table 3: Differential Morphology of Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Amoebae-Trophozoites
| NUCLEUS | CYTOPLASM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Size (Length) | Motility | Number | Peripheral Chromatin | Karyosomal Chromatin | Appearance | Inclusions |
| Entamoeba histolytica | 10-60 µm. Usual range, 15-20 µm commensal form.1 Over 20 µm invasive form.2 | Progressive with hyaline, finger-like pseudopods. | 1 Not visible in unstained preparations. |
Fine granules. Usually evenly distributed and uniform in size. | Small, discrete. Usually centrally located, but occasionally is eccentric. | Finely granular. | Red blood cells occasionally. Noninvasive organisms may contain bacteria. |
| Entamoeba hartmanni | 5-12µm. Usual range, 8-10 µm. | Usually nonprogressive but may be progressive occasionally. | 1 Not visible in unstained preparations. |
Similar to E. histolytica. |
Small, discrete, often eccentric. | Finely granular. | Bacteria. |
| Entamoeba coli | 15-50µm. Usual range, 20-25 µm. | Sluggish, nonprogressive, with blunt pseudopods. | 1 Often visible in unstained preparations. |
Coarse granules, irregular in size and distribution. | Large, discrete, usually eccentric. | Coarse, often vacuolated. | Bacteria, yeasts, other materials. |
| Entamoeba polecki | 10-25µm. Usual range, 15-20 µm. | Usually sluggish, similar to E. coli. Occasionally, in diarrheic specimens, motility may be progressive. | 1 May be slightly visible in unstained preparations. Occasionally may be irregularly distorted by pressure from vacuoles in cytoplasm. |
Usually fine granules evenly distributed. Occasionally granules may be irregularly arranged. Chromatin sometimes in plaques or crescents. | Small, discrete, eccentric. Occasionally large, diffuse or irregular. | Coarsely, granular, may resemble E. coli. Contains numerous vacuoles. | Bacteria, yeasts. |
| Endolimax nana | 6-12 µm. Usual range, 8-10 µm. | Sluggish, usually nonprogressive with blunt pseudopods. | 1 Visible occasionally in unstained preparations. |
None. | Large, irregularly shaped, blot-like. | Granular, vacuolated. | Bacteria. |
| Iodamoeba buetschlii | 8-20 µm. Usual range, 12-15 µm. | Sluggish, usually nonprogressive. | 1 Not usually visible in unstained preparations. |
None. | Large, usually central. Surrounded by refractile, achromatic granules. These granules are often not distinct even in stained slides. | Coarsely granular, vacuolated. | Bacteria, yeasts, or other material. |
| Dientamoeba fragilis3 | 5-15 µm. Usual range, 9-12 µm. | Pseudopods are angular, serrated, or broad lobed, and hyaline, almost transparent. | 2 (In approximately 20% of organisms only 1 nucleus is present.) Nuclei invisible in unstained preparations. |
None. | Large cluster of 4-8 granules. | Finely, granular. | Bacteria: occasionally red blood cells. |
Table 4: Differential Morphology of Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Amoebae-Cysts
| NUCLEUS | CYTOPLASM | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Size (Diameter or Length) | Shape | Number | Peripheral Chromatin | Karyosomal Chromatin | Inclusions | Appearance |
| Entamoeba histolytica | 10-20 µm Usual range, 12-15 µm. |
Usually spherical. | 4 in mature cyst. Immature cysts with 1 or 2 occasionally seen. | Peripheral chromatin present. Fine, uniform granules, evenly distributed. | Small, discrete, usually centrally located. | Present. Elongated bars with bluntly rounded ends. | Usually diffuse. Concentrated mass often present in young cysts. Stains reddish brown with iodine. |
| Entamoeba hartmanni | 5-10 µm Usual range, 6-8 µm. |
Usually spherical. | 4 in mature cyst. Immature cysts with 1 or 2 often seen. | Similar to E. histolytica. | Similar to E. histolytica. | Present. Elongated bars with bluntly rounded ends. | Similar to E. histolytica. |
| Entamoeba coli | 10-35 µm Usual range, 15-25 µm. |
Usually spherical. Occasionally oval, triangular, or other shapes. | 8 in mature cyst. Occasionally super-nucleated cysts with 16 or more are seen. Immature cysts with 2 or more occasionally seen. | Peripheral chromatin present. Coarse granules irregular in size and distribution, but often appear more uniform than in trophozoites. | Large, discrete, usually eccentric but occasionally centrally located. | Present, but less frequently seen than in E. histolytica. Usually splinter-like with pointed ends. | Usually diffuse, but, occasionally well defined mass in immature cysts. Stain reddish brown with iodine. |
| Entamoeba polecki | 9-18 µm Usual range, 11-15 µm. |
Spherical or oval. | 1. Rarely 2. Occasionally visible in unstained preparations. | Usually fine granules evenly distributed. | Usually small and eccentric. | Present. Many small bodies with angular or pointed ends, or few large ones. May be oval, rod-like, or irregular. | Usually small, diffuse masses stain reddish brown with iodine. A dark area called an “inclusion mass” (possibly concentrated cytoplasm) is often also present. Mass stains lightly with iodine. |
| Endolimax nana | 5-10 µm. Usual range, 6-8 µm. |
Spherical to Oval | Four in mature cysts; not seen in unstained preparations | None. | Large (blot-like), usually central. | Occasionally granules or small oval masses seen, but bodies as seen in Entamoeba spp. are not present. | Usually diffuse. Concentrated mass seen occasionally in young cysts. Stains reddish brown with iodine. |
| Iodamoeba buetschlii | 5-20 µm. Usual range, 10-12 µm | Ovoidal, ellipsoidal, triangular, or other shapes. | 1 in mature cyst. | None. | Large, usually eccentric. Refractile, achromatic granules on one side of karyosome. Indistinct in iodine preparations. | Occasionally granules present, but chromatoid bodies as seen in Entamoeba spp. are not present. | Compact, well-defined mass. Stains dark brown with iodine. |
Table 5: Differential Morphology of Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Flagellates-Trophozoites
| Species | Size (Length) | Shape | Motility | Number of Nuclei | Number of Flagella* | Other Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pentatrichomonas hominis | 6-20 µm. Usual range. 11-12 µm. |
Pear shaped. | Nervous, jerky. | 1 Not visible in unstained mounts. |
3-5 anterior. 1 posterior. |
Undulating membrane extending length of body. |
| Chilomastix mesnili | 6-24 µm. Usual range, 10-15 µm. |
Pear shaped. | Stiff, rotary. | 1 Not visible in unstained mounts. |
3 anterior. 1 in cytosome. |
Prominent cytostome extending 1/3-1/2 length of body. Spiral groove across ventral surface. |
| Giardia duodenalis | 10-20 µm. Usual range, 12-15 µm. |
Pear shaped. | “Falling leaf.” | 2 Not visible in unstained mounts. |
4 lateral. 2 ventral. 2 caudal. |
Sucking disk occupying 1/2-3/4 of ventral surface. Median bodies lying horizontally or obliquely in lower part of body. |
| Enteromonas hominis | 4-10 µm. Usual range, 8-9 µm. |
Oval. | Jerky. | 1 Not visible in unstained mounts. |
3 anterior. 1 posterior. |
One side of body flattened. Posterior flagellum extends free posteriorly or laterally. |
| Retortamonas intestinalis | 4-9 µm. Usual range, 6-7 µm. |
Pear shaped or oval. | Jerky. | 1 Not visible in unstained mounts. |
1 anterior. 1 posterior. |
Prominent cytostome extending approximately 1/2 length of body. |
*Not a practical feature for identification of species in routine fecal examinations
Table 6: Differential Morphology of Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Flagellates-Cysts
| Species | Size (Length) | Shape | Number of Nuclei | Other Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pentatrichomonas hominis | No cyst. | |||
| Chilomastix mesnili | 6-10 µm. Usual range, 8-9 µm. |
Lemon shaped with anterior hyaline knob. | 1. Not visible in unstained preparations. | Cytostome with supporting fibrils. Usually visible in stained preparations. |
| Giardia duodenalis | 8-19 µm. Usual range. 11-12 µm. |
Oval or ellipsoidal. | Usually 4. Not distinct in unstained preparations. Usually located at one end. | Fibrils or flagella longitudinally in unstained cysts. Deep staining fibers or fibrils may be seen lying laterally or obliquely across fibrils in lower part of cyst. Cytoplasm often retracts from a portion of cell wall. |
| Enteromonas hominis | 4-10 µm. Usual range, 6-8 µm. |
Elongated or oval. | 1-4, usually 2 lying at opposite ends of cyst. Not visible in unstained mounts. | Resembles E. nana cyst. Fibrils or flagella are usually not seen. |
| Retortamonas intestinalis | 4-9 µm. Usual range, 4-7 µm. |
Pear shaped or slightly lemon shaped. | 1. Not visible in unstained mounts. | Resembles Chilomastix cyst. Shadow outline of cytostome with supporting fibrils extends above nucleus. |
Table 7: Differential Morphology of Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Ciliates, Coccidia, and Blastocystis
| Species | Stage | Size | Shape | Motility | Number of Nuclei | Other Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balantidium coli | Trophozoite | 50-70 µm or more. Usual range, 40-50 µm. | Ovoid with tapering anterior end. | Rotary, boring. | 1 large, kidney shaped macronucleus. 1 small micronucleus immediately adjacent to macronucleus. Macronucleus occasionally visible in unstained preparations as hyaline mass. | Body surface covered by spiral, longitudinal rows of cilia. Contractile vacuoles are present. |
| Cyst | 45-65 µm. Usual range, 50-55 µm. | Spherical or oval. | 1 large macronucleus visible in unstained preparations as hyaline mass. | Macronucleus and contractile vacuole are visible in young cysts. In older cysts, internal structure appears granular. | ||
| Cystoisospora belli | Oocyst | 25-30 µm. Usual range, 28-30 µm. | Ellipsoidal | Nonmotile | Usual diagnostic stage is immature oocyst with single granular mass (zygote) within. Mature oocyst contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites each. | |
| Sarcocystis hominis | Sporocyst1 | 13-17 µm. Usual range, 14-16 µm. | Oval | Nonmotile | Mature oocysts with thin wall collapsed around 2 sporocysts or free fully mature sporocysts with 4 sporozoites inside are usually seen in feces. | |
| Sarcocystis suihominis | Sporocyst1 | 1-15 µm. Usual range, 12-13 µm. |
Oval | Nonmotile | Mature oocysts with thin wall collapsed around 2 sporocysts or free fully mature sporocysts with 4 sporozoites inside are usually seen in feces. | |
| Cryptosporidium | Oocyst | 3-6 µm. Usual range, 4-5 µm. |
Spherical or oval. | Nonmotile | Mature oocyst contains 4 “naked” sporozoites. No sporocysts are present. | |
| Blastocystis hominis2 | Vacuolated Form | 5-30 µm. Usual range, 8-10 µm. |
Spherical, oval, or ellipsoidal | Nonmotile | 1, usually, but 2-4 may be present. Located in “rim” of cytoplasm. In binucleated organisms, the 2 nuclei may be at opposite poles. In quadrinucleated forms, the 4 nuclei are evenly spaced around periphery of cell. | Cell contains large central body, or “vacuole” with a thin band, or “rim” of cytoplasm around the periphery. Occasionally a ring of granules may be seen in cytoplasm and the cell appears to have a “beaded rim.” |
- Sizes are based on information from Rommel and Heydorn (1972) and Heydorn et al. (1975).
- Description based on information from Zierdt, 1973 and McClure et al., (1980).
Table 8a (Nematodes): Differential Morphology of the Diagnostic Stages of Helminths Found in Humans: Eggs (Nematodes)
| Species | Size | Shape | Color | Stage of Development When Passed | Specific Features And Variations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enterobius vermicularis | 55 µm x 26 µm Range, 50-60 µm 20-32 µm. | Elongated, asymmetrical with one side flattened, other side convex. | Colorless. | Embryonated. Contains C shaped or tadpole-like embryo. | Smooth, thin eggshell with one flattened side. Occasionally may contain a fully developed larva. (More readily found on anal swabs than in feces). |
|
Ascaris lumbricoides fertile egg |
60 µm x 45 µm. Range, 45-70 µm x 35-45 µm. | Round or ovoidal. with thick shell. | Brown or yellow brown. | 1 cell, separated from the shell at both ends. | Mammillated albuminous coat or covering on outer shell. Coat is sometimes lost and decorticated eggs have a colorless shell with gray or black internal material. Eggs may be in 2, 4, or more cells, or contain a fully developed larva. |
|
Ascaris lumbricoides infertile egg |
90 µm x 40 µm. Range, 85-95 µm x 35-45 µm. | Elongated, occasionally triangular, kidney shaped or other bizarre forms. Shell often very thin. | Brown. | Internal material is a mass of irregular globules and granules that fills shell. | Mammillated covering attenuated or missing in many cases. |
| Trichuris trichiura | 54 µm x 22 µm. Range, 49-65 µm x 20-29 µm. | Elongated, barrel-shaped with a polar “plug” at each end. | Yellow to brown. “Plugs” are colorless. | 1 cell or unsegmented. | Polar plugs are distinctive. Eggs occasionally are oriented in a vertical or slanted position and may not be readily recognized. A gentle tap on the coverslip will usually reorient the egg. On rare occasions, atypical eggs lacking polar plugs may be seen. |
| Ancylostoma duodenale | 60 µm x 40 µm. Range, 57-76 µm x 35-47 µm. | Oval or ellipsoidal with a thin shell. | Colorless with grayish cells. | 4- to 8-cell stage. | Occasionally, eggs in advanced cleavage (16 or more cells) or even embryonated may be seen. Rhabditiform larvae may be present if the specimens are old. Species identification can not be made on eggs alone; therefore, eggs should be reported simply as hookworm. |
| Necator americanus | 65 µm x 40 µm. Range, 57-76 µm x 35-47 µm. | Oval or ellipsoidal with a thin shell. | Colorless with grayish cells. | 4- to 8-cell stage. | Occasionally, eggs in advanced cleavage (16 or more cells) or even embryonated may be seen. Rhabditiform larvae may be present if the specimens are old. Species identification can not be made on eggs alone; therefore, eggs should be reported simply as hookworm. |
| Trichostrongylus species | 90 µm x 40 µm. Range, 75-95 µm x 40-50 µm. | Elongated with one or both ends more pointed than hookworm. | Colorless with grayish cells. | May be in advanced cleavage or morula stage. | Egg resembles hookworm egg but is larger and more pointed at the ends. |
Table 8b (Cestodes): Differential Morphology of the Diagnostic Stages of Helminths Found in Humans: Eggs (Cestodes)
| Species | Size | Shape | Color | Stage of Development When Passed | Specific Features and Variations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taenia saginata Taenia solium | 35 µm. Range, 31-43 µm. | Spherical with thick striated shell. | Walnut brown. | Embryonated. 6-hooked oncosphere present inside a thick shell. | Thick, striated shell. Eggs of T. solium and T. saginata are indistinguishable and species identification should be made from proglottids or scoleces. “Taenia” spp. should be reported if only eggs are found. |
| Hymenolepis nana | 47 µm x 37 µm. Range, 40-60 µm x 30-50 µm. | Oval. Shell consists of 2 distinct membranes. On inner membrane are two small “knobs” or poles from which 4 to 8 filaments arise and spread out between the two membranes. | Colorless, almost transparent. | Embryonated. 6-hooked oncosphere inside shell. | Polar filaments. |
| Hymenolepis diminuta | 72 µm. Range, 70-86 µm x 60-80 µm. | Round or slightly oval. Striated outer membrane and thin inner membrane with slight poles. Space between membranes may appear smooth or faintly granular. | Yellow. | Embryonated. 6-hooked oncosphere inside shell. | Resembles H. nana but lacks polar filaments. Poles are rudimentary and often hard to see. |
| Dipylidium caninum | 35-40 µm. Range, 31-50 µm x 27-48 µm. | Spherical or oval. 5-15 eggs (or more) are enclosed in a sac or capsule. | Colorless. | Embryonated. 6-hooked oncosphere inside shell. | Eggs are contained in a sac or capsule which ranges in size from 58 µm to 60 µm x 170 µm. Occasionally capsules are ruptured and eggs are free. |
| Diphyllobothrium latum | 66 µm x 44 µm. Range, 58-76 µm x 40-51 µm. | Oval or ellipsoidal with an inconspicuous operculum at one end and a small “knob” at the other end. | Yellow to brown. | Unembryonated. Germinal cell is surrounded by a mass of yolk cells which completely fills inner area of shell. Germinal cell is usually not visible. | Egg resembles hookworm egg but has a thicker shell and an operculum. |
Table 8c (Trematodes): Differential Morphology of the Diagnostic Stages of Helminths Found in Humans: Eggs (Trematodes)
| Species | Size | Shape | Color | Stage of Development When Passed | Specific Features and Variations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schistosoma mansoni | 140 µm x 66 µm. Range, 114-180 µm x 45-73 µm. | Elongated with prominent lateral spine near posterior end. Anterior end tapered and slightly curved. | Yellow or yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Lateral spine. Found in feces; in rare cases, in urine also. Eggs are discharged at irregular intervals and may not be found in every stool specimen. Are rare in chronic stages of infection. |
| Schistosoma japonicum | 90 µm x 70 µm. Range, 68-100 µm x 45-80 µm. | Oval. Small lateral spine is often seen or may appear as a small hook or “knob” located in a depression in the shell. | Yellow or yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Found in feces. Often coated with debris and may be overlooked. |
| Schistosoma haematobium | 143 µm x 60 µm. Range, 112-170 µm x 40-70 µm. | Elongated with rounded anterior end and terminal spine at posterior end. | Yellow or yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Terminal spine. Found in urine, occasionally in feces. Egg often covered with debris. |
| Schistosoma intercalatum | 175 µm x 60 µm. Range, 140-240 µm x 50-85 µm. | Elongated with tapered anterior end and terminal spine. Sometimes “spindle-shaped.” | Yellow or yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Terminal spine long, slender with bent tip. Resembles S. haematobium egg except it is longer, is thinner, and has a longer spine. Found in feces. May have debris adhering to shell. |
| Schistosoma mekongi | 69 µm x 56 µm* Range, 51-73 µm x 39-66 µm. | Spherical. Small lateral spine, not always visible or may appear as a small “knob” in a depression in the shell. | Yellow or yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Found in feces. Closely resembles S. japonicum egg except it is smaller. May be coated with debris. |
| Clonorchis sinensis | 30 µm x l6 µm. Range, 27-35 µm x 11-20 µm. | Small, ovoidal, or elongated with broad rounded posterior end and a convex operculum resting on “shoulders.” A small “knob” may be seen on the posterior end. | Yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Small size, operculum and “knob” on posterior end. Shell often is covered by adhering debris. |
| Opisthorchis spp. | 30 µm x 12 µm. Range, 26-30 µm x 11-15 µm. | Elongated with operculum on anterior end and pointed terminal “knob” on posterior end. | Yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Lacks prominent shoulders characteristic of Clonorchis and has more tapered end. |
| Heterophyes heterophyes | 28 µm x 15 µm. Range, 28-30 µm x 15-17 µm. | Small, elongated or slightly ovoidal. Operculum. Slight “knob” at posterior end. | Yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Resembles Clonorchis egg but with less distinct shoulders. Operculum is broader than in Clonorchis. |
| Metagonimus yokogawai | 28 µm x 17 µm. Range, 26-30 µm x 15-20 µm. | Small, elongated or ovoidal. Operculum. No “shoulders” at anterior end. Small “knob” often seen on posterior end. | Yellow or yellow brown. | Embryonated. Contains mature miracidium. | Resembles Clonorchis and Heterophyes eggs. Shell is slightly thinner than Heterophyes. Operculum is broader than Clonorchis. |
| Paragonimus westermani | 85 µm x 53 µm. Range, 68-118 µm x 39-67 µm. | Ovoidal or elongate with thick shell. Operculum is slightly flattened and fits into shoulder area of shell. Posterior end is thickened. Egg often asymmetrical with one side slightly flattened. | Yellow brown to dark brown. | Unembryonated. Filled with yolk material in which a germinal cell is imbedded. Cells are irregular in size. | Found in sputum, occasionally in feces. Resembles egg of D. latum but is larger, slightly asymmetrical and the operculum is smaller and flatter. The widest part of the Paragonimus egg is usually anterior to the center ; in a D. latum, the widest area is around the center. |
| Fasciola hepatica | 145 µm x 80 µm. Range, 120-150 µm x 63-90 µm. | Ellipsoidal, thin shell. Small, indistinct operculum. | Yellow to light brown. | Unembryonated. Filled with yolk cells in which an indistinct germinal cell is imbedded. | Large size. Broadly oval eggs. |
| Fasciolopsis buski | 140 µm x 80 µm. Range, 130-159 µm x 78-98 µm. | Ellipsoidal, thin shell. Small, indistinct operculum. | Yellow brown. | Unembryonated. Filled with yolk cells in which an indistinct germinal cell is imbedded. | Large size. Resembles F. hepatica egg and cannot be easily distinguished from Fasciola. |
*Based on sizes of eggs in human fecal specimens reported by Harinasuta and Kruatrachue (1962) and Taylor and Moose (1971).
Table 9: Differential Morphology of the Diagnostic Stages of Helminths Found in Humans: Larvae
| RHABDITIFORM LARVA (First Stage. Has bulbed esophagus.) | FILARIFORM LARVA (Third Stage. Lacks prominent bulb in esophagus.) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
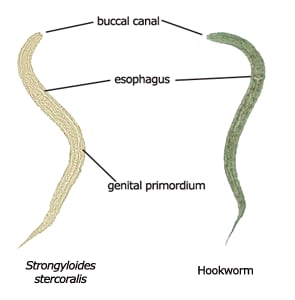
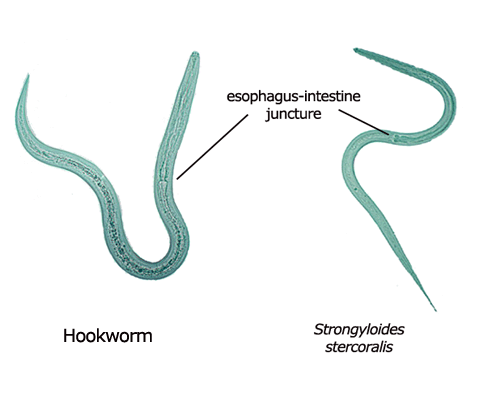
| Species | Size | Genital Primordium | Buccal Cavity | Size | Length of Esophagus | Tip of Tail |
| Strongyloides stercoralis | 225 µm × 16 µm. Range, 200- 300 µm × 16-20 µm. | Prominent. Is an elongate, tapered, or pointed structure located along ventral wall about the body length. | Short, about 1/3-1/2 as long as the width of the anterior end of the body. | 550 µm × 20 µm. Range, 500-550 µm × 20-24 µm. | Extends approximately 1/2 length of body. | Notched. |
| Hookworm | 250 µm × 17 µm. Range, 200- 300 µm × 14-17 µm. | Inconspicuous. Rarely distinct. When seen, is small, located nearer the tail than that of Strongyloides. | Long. Approximately as long as the width of the body. | 500 µm. Range, 500-700 µm × 20-24 µm. | Extends about 1/4 1ength of body. | Pointed. |
Table 10: Differential Morphology of the Diagnostic Stages of Helminths Found in Humans: Tapeworm Gravid Proglottids
| Species | Size | Appearance of Uterus | Other |
|---|---|---|---|
| Taenia solium | 12 mm in length x 5-7 mm wide. | Central “stem” or trunk with 7-13 main lateral branches on each side. | Usually on surface of fecal material. May be in short chains of 2-3 proglottids. |
| Taenia saginata | 16-20 mm long × 5-7 mm wide. | Central “stem” or trunk with 15-20 main lateral branches on each side. | Usually on surface of fecal material. May be single detached proglottids. |
| Diphyllobothrium latum | 2-4 mm long × 10-12 mm wide. Broader than long. | Coiled into a rosette appearance. | Occasionally, portion of worm may be passed. Egg is usual diagnostic stage. |
| Dipylidium caninum | 12 mm long × 3 mm wide. Pumpkin-seed shape; tapers at each end. | Uterus not visible. Proglottid filled with capsules containing eggs. | Proglottids may be passed singly or in chains. Often resemble rice grains in stool. |
| Hymenolepis nana | 0.2-0.3 mm long x 0.8-0.9 mm wide. Broader than long. | Uterus not visible. Proglottid filled with eggs. | Proglottids usually disintegrate in the intestinal tract and are rarely seen in stools. Egg is usual diagnostic stage. |
| Hymenolepis diminuta | 0.7-0.8 mm long × 3-4 mm wide. Broader than long. | Uterus not visible. Proglottid filled with eggs. | Proglottids usually disintegrate in the intestinal tract and are rarely seen in stools. Egg is usual diagnostic stage. |
Table 11: Differential Morphology of the Diagnostic Stages of Helminths Found in Humans: Tapeworm Scoleces
| Species | Size | Shape | Suckers No. | Appearance | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taenia solium | Approximately 1 mm in diameter. | Globular or rounded. | 4 | Cup-like. | Double row of 25-30 large and small brown chitinous hooks arranged around a rostellum (small projection) at the top of the scolex. |
| Taenia saginata | 1 to 2 mm in diameter. | Rounded or slightly pyriform. | 4 | Cup-like. | Does not have a rostellum or hooks. |
| Diphyllobothrium latum | 2 to 3 mm in length × 1 mm wide. | Almond-shaped or spatulate. | 2 | Grooves. | Does not have a rostellum or hooks. Deep grooves (suckers) are located dorsally and centrally on the scolex, but often appear to be lateral. |
| Dipylidium caninum | 0.35 × 0.37 mm. | Rhomboid or rounded. | 4 | Oval, cup-like. | Prominent conical or ovoid rostellum with 30-150 small thorn-shaped hooks arranged in several rows (1-7 rows). Rostellum may be retracted into a depression at the upper margin of the scolex. |
| Hymenolepis nana | 0.3 mm in diameter. | Globular. | 4 | Cup-like. | Retractile rostellum with a single row of 20 to 30 hooks. |
| Hymenolepis diminuta | 0.2-0.4 mm in diameter. | Globular or club-shaped. | 4 | Cup-like. | Rudimentary apical rostellum without hooks. |
Intestinal Parasites: Comparative Morphology Figures
Figure 1: Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Amebae
| Stage | Entamoeba histolytica/dispar | Entamoeba hartmanni | Entamoeba coli | Entamoeba polecki | Endolimax nana | Iodamoeba beutschlii |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trophozoite | 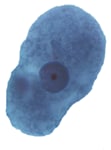 |
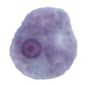 |
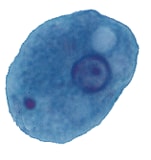 |
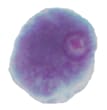 |
 |
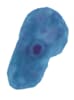 |
| Cyst | 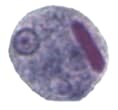 |
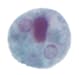 |
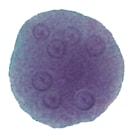 |
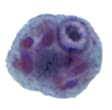 |
 |
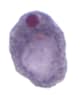 |
 |
 |
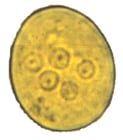 |
 |
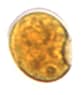 |
 |
Figure 2: Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Ciliates and Flagellates
| Stage | Ciliate  40 µm 40 µm |
Flagellates  10 µm 10 µm |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balantidium coli | Chilomastix mesnili | Giardia duodenalis | Dientamoeba fragilis | |
| Trophozoite | 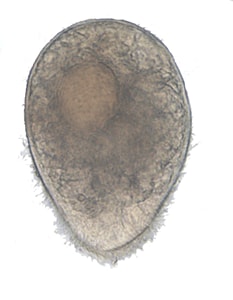 |
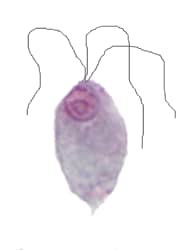 |
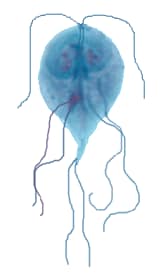 |
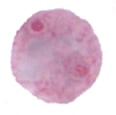 |
| Cyst | 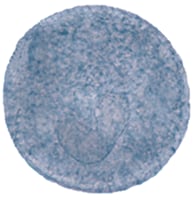 |
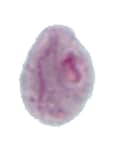 |
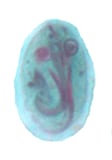 |
no cyst stage |
 |
 |
|||
Figure 3: Protozoa Found in Stool Specimens of Humans: Coccidia and Blastocystis
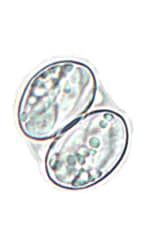
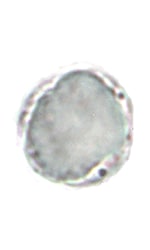
| Coccidia | Blastocystis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cystoisospora belli | Sarcocystis spp. | Cryptosporidium spp. | Cyclospora cayetanensis | Blastocystis hominis |
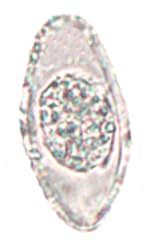 wet mount wet mount |
 oocyst oocyst |
 wet mount wet mount |
 wet mount wet mount |
 wet mount wet mount |
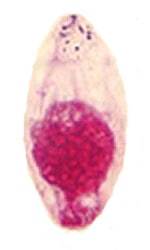 safranin safranin |
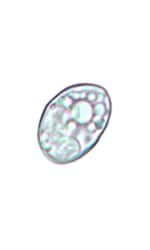 sporocyst sporocyst |
 acid-fast acid-fast |
 acid-fast acid-fast |
 trichrome trichrome |
Figure 4: Nematode and Cestode Eggs Found in Stool Specimens of Humans
| Nematodes |
 Capillaria philippinensis Capillaria philippinensis
|
 Enterobius vermicularis Enterobius vermicularis
|
 Trichuris trichiura Trichuris trichiura
|
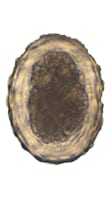 Ascaris lumbricoides Ascaris lumbricoidesfertile |
 Ascaris lumbricoides Ascaris lumbricoidesinfertile |
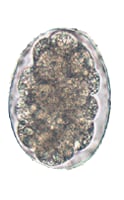 Hookworm Hookworm |
 Trichostrongylus spp. Trichostrongylus spp. |
|---|
| Cestodes |
 Taenia spp. Taenia spp. |
 Hymenolepis nana Hymenolepis nana
|
 Hymenolepis diminuta Hymenolepis diminuta
|
 Diphyllobothrium latum Diphyllobothrium latum
|
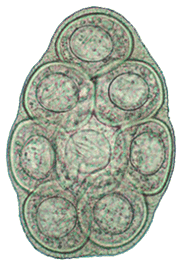 Dipylidium caninum Dipylidium caninum
|
|---|
![]()
Figure 5: Trematode Eggs Found in Stool Specimens of Humans
| Trematodes |
|||
|---|---|---|---|
 Clonorchis sinensis Clonorchis sinensis
|
 Opisthorchis viverrini Opisthorchis viverrini
|
 Paragonimus westermani1 Paragonimus westermani1
|
 Nanophyetus salmincola Nanophyetus salmincola
|
 Schistosoma japonicum Schistosoma japonicum
|
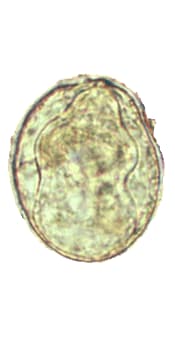 Schistosoma mekongi Schistosoma mekongi
|
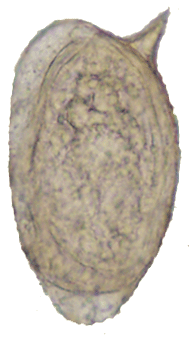 Schistosoma mansoni Schistosoma mansoni
|
 Schistosoma intercalatum Schistosoma intercalatum
|
 Schistosoma haematobium2 Schistosoma haematobium2
|
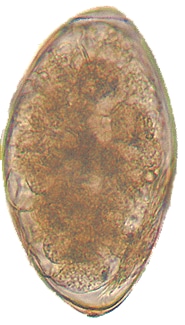 Fasciola hepatica Fasciola hepatica
|
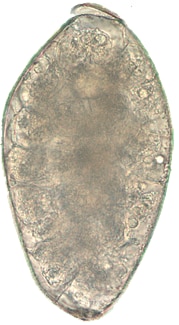 Fasciolopsis buski Fasciolopsis buski
|
 Echinostoma spp. Echinostoma spp. |
- Usually found in respiratory specimens.
- Usually passed in urine.
Figure 6: Relative Sizes of Helminth Eggs
Measurements in micrometers (µm)
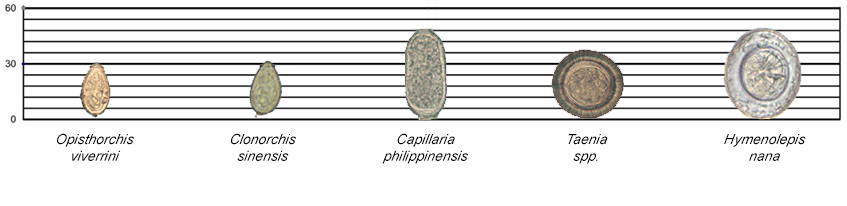
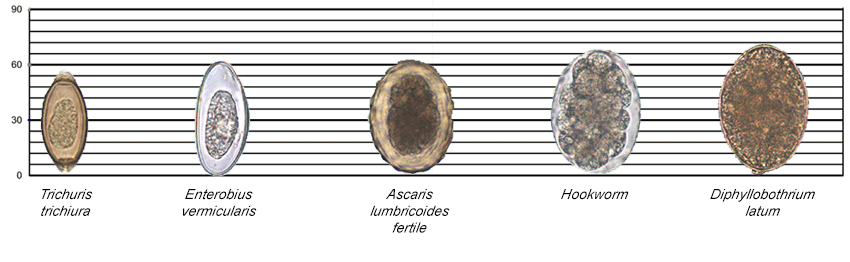
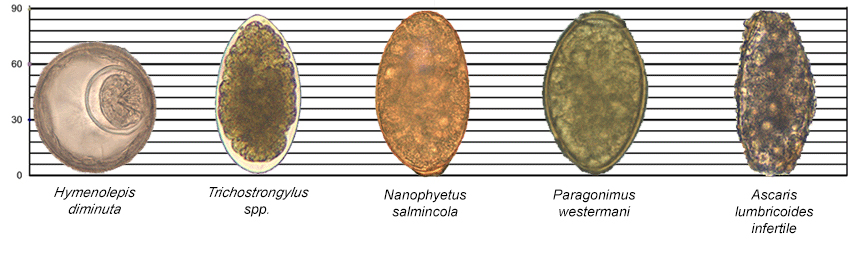

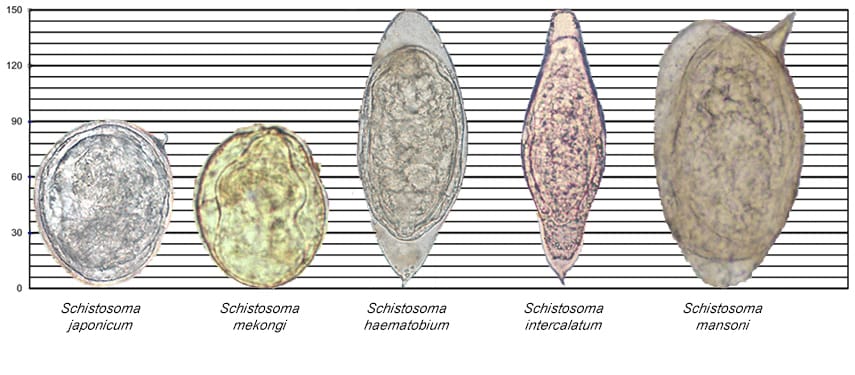
Figure 7: Hookworm and Strongyloides Larvae
| Rhabditiform (L1) Stage | Filariform (L3) Stage |
|---|---|
 |
 |
![]()
Figure 8: Gravid Proglottids and Scoleces of Cestode Parasites of Humans
Note: figures are not shown to scale.

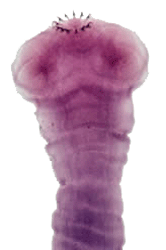
Taenia solium
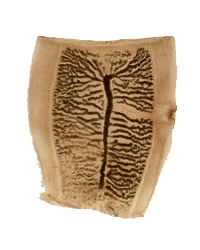
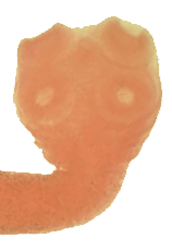
Taenia saginata
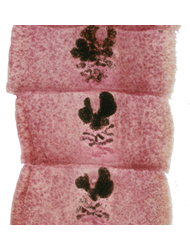
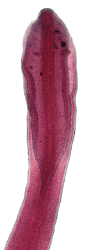
Diphyllobothrium latum
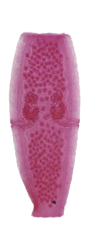
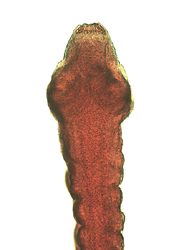
Dipylidium caninum

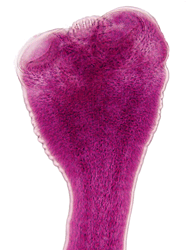
Hymenolepis nana


Hymenolepis diminuta
Figure 9: Adult Visceral Trematodes of Humans
DPDx is an educational resource designed for health professionals and laboratory scientists. For an overview including prevention, control, and treatment visit www.cdc.gov/parasites/.