Key points
- Symptoms of candidiasis depend on what part of the body is infected.
- Infections and symptoms can affect the vagina (yeast infection), the mouth and throat, or the esophagus.
- Invasive candidiasis causes fever and chills and can cause different symptoms if it spreads to organs, bones, or joints.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the part of the body that is infected. Different types of infections can cause similar symptoms. Healthcare providers can test to see if you have candidiasis.
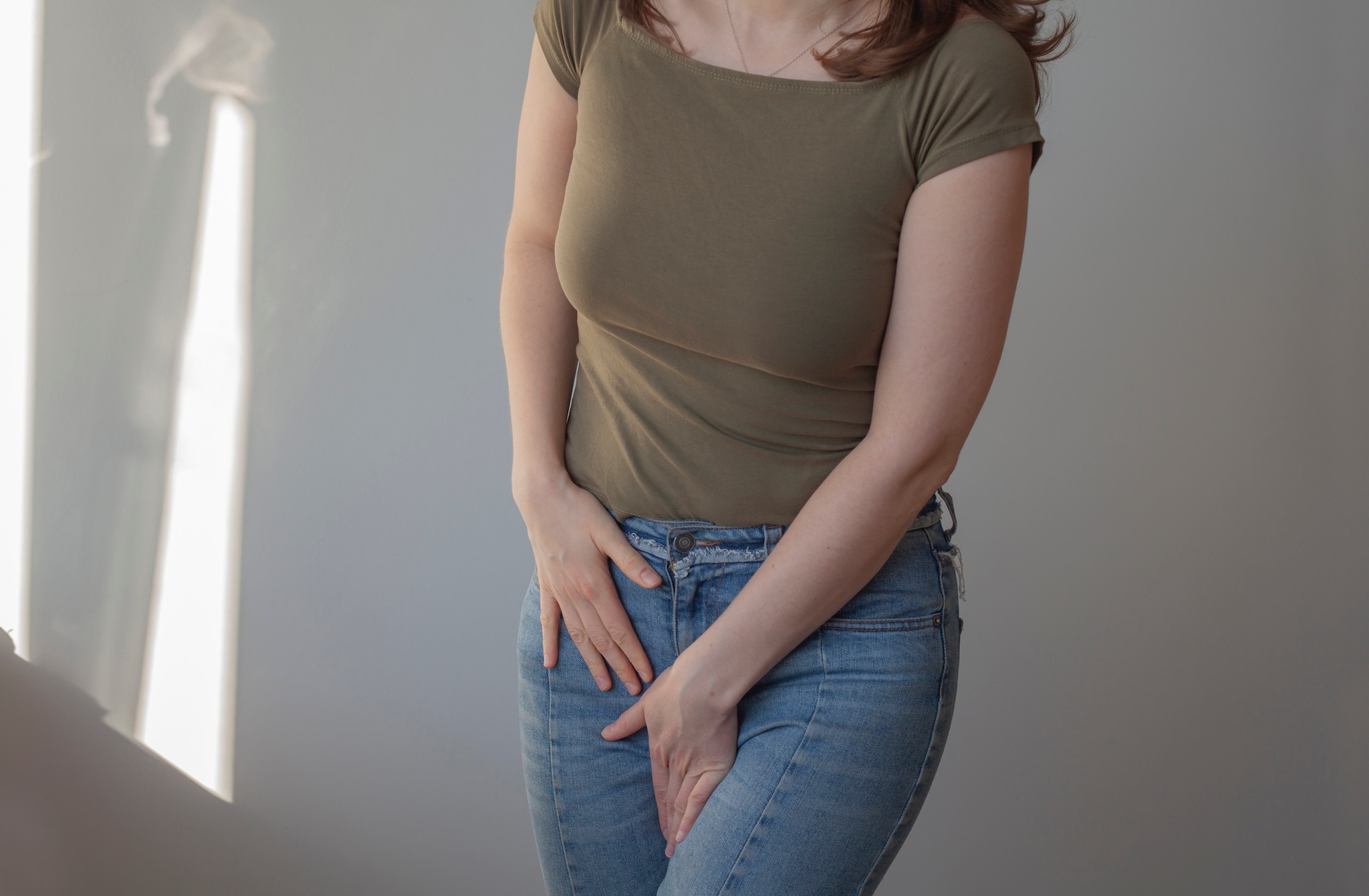
Vaginal candidiasis (yeast infection)
The symptoms of vaginal candidiasis include:
- Vaginal itching or soreness
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Pain or discomfort when urinating
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
Vaginal candidiasis is often mild. However, some women can develop severe infections involving redness, swelling, and cracks in the wall of the vagina.

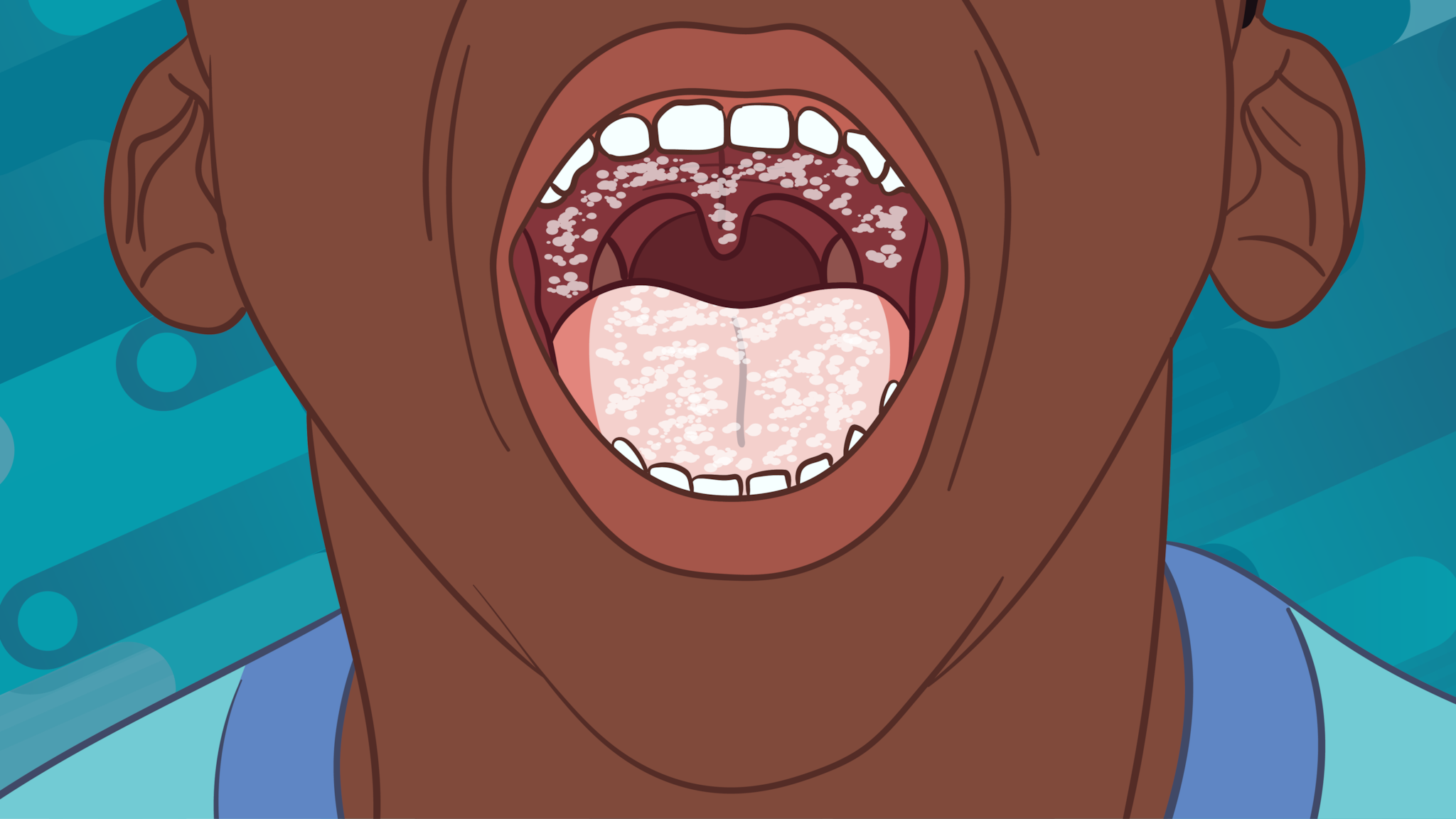
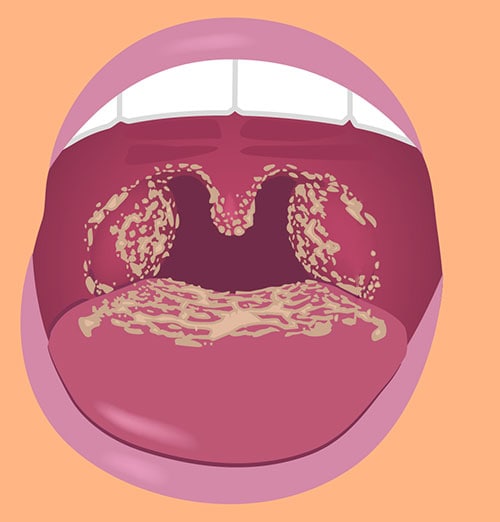
Candidiasis of the mouth and throat (thrush) and esophagus
Candidiasis in the mouth and throat can have many different symptoms, including:
- White patches on inner cheeks, tongue, roof of the mouth, and throat.
- Redness or soreness
- Cotton-like feeling in the mouth
- Loss of taste
- Pain while eating or swallowing
- Cracking and redness at the corners of the mouth
Symptoms of candidiasis of the esophagus include pain and difficulty swallowing. Most people who get candidiasis of the esophagus also have mouth and throat infections.
Invasive candidiasis
Most people are not at risk for invasive candidiasis, including candidemia (bloodstream infections). People who develop invasive candidiasis are often already sick from other medical conditions, so it can be difficult to know which symptoms are related to a Candida infection.
The most common symptoms of invasive candidiasis are fever and chills that don't improve after antibiotic treatment for suspected bacterial infections.
Other symptoms can develop if the infection spreads to other parts of the body, such as the heart, brain, eyes, bones, or joints.
