Key points
- Anencephaly (an-en-sef-ah-lee) is a serious birth defect where a baby is without parts of the brain and skull at birth.
- Almost all babies born with anencephaly will die shortly after birth.
- Researchers estimate that about 1 in every 5,250 babies has anencephaly in the United States.
What it is
Anencephaly is where a baby is without parts of the brain and skull at birth. It is fatal and there is no cure or treatment.
Anencephaly is a type of neural tube defect (NTD). During early pregnancy, the neural tube develops into the baby's brain and spine. The upper part helps form the baby's brain and skull, and the lower part forms the spinal cord and back bones.
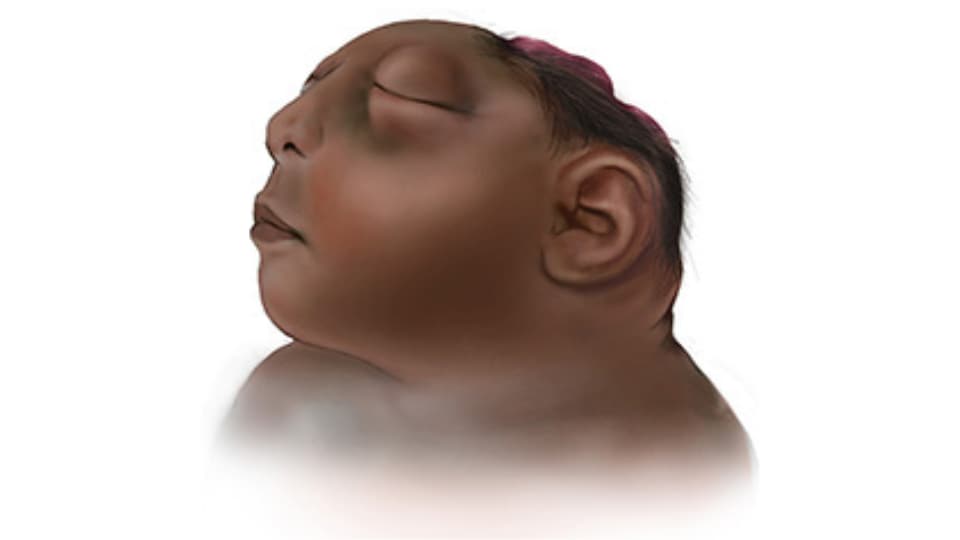
In anencephaly, the upper part of the neural tube does not close all the way. At birth, the baby often has no
- front part of the brain (forebrain)
- thinking and coordinating part of the brain (cerebrum)
- bone or skin covering the remaining parts of the brain.
Risk factors
We do not know all the causes of anencephaly, but certain factors can affect the chances of a baby having anencephaly. Examples are a change in the baby’s genes or a combination of genes and other factors.
Researchers have identified factors in pregnant people that might increase the chance for anencephaly:
- Low folate (vitamin B9) levels during early pregnancy1
- Pre-existing health conditions, such as diabetes, that are not well controlled
- Certain medications, such as antiseizure medications
- Overheating (like getting in a hot tub) or fever
Importance of Folic Acid
Screening and diagnosis
Healthcare providers may diagnose anencephaly during pregnancy or after birth.
During pregnancy
During pregnancy, there are tests to check for birth defects and other conditions. Being pregnant with a baby with anencephaly can result in an abnormal result on a blood or serum test. Anencephaly can also be seen during an ultrasound exam.
After birth
In some cases, anencephaly might not be diagnosed until after birth. At that time. healthcare providers can see anencephaly immediately.
Expected outcomes
There is no known cure or standard treatment for anencephaly. Pregnancy loss is high. Almost all babies born with anencephaly will die shortly after birth.
- Crider KS, Qi YP, Yeung LF, Mai CT, Head Zauche L, Wang A, Daniels K, Williams JL. Folic Acid and the Prevention of Birth Defects: 30 Years of Opportunity and Controversies. Annu Rev Nutr. 2022 Aug 22;42:423-452.
- Stallings, E. B., Isenburg, J. L., Rutkowski, R. E., Kirby, R. S., Nembhard, W.N., Sandidge, T., Villavicencio, S., Nguyen, H. H., McMahon, D. M., Nestoridi, E., Pabst, L. J., for the National Birth Defects Prevention Network. National population-based estimates for major birth defects, 2016–2020. Birth Defects Research. 2024 Jan;116(1), e2301.
