Key points
- Burkholderia cepacia complex, also called B. cepacia or Bcc, is a group of bacteria that can cause infections in healthcare settings.
- Good infection control practices, including around the use of water, can help reduce infection risk.
- B. cepacia germs can be resistant to antibiotics, making them difficult to treat.
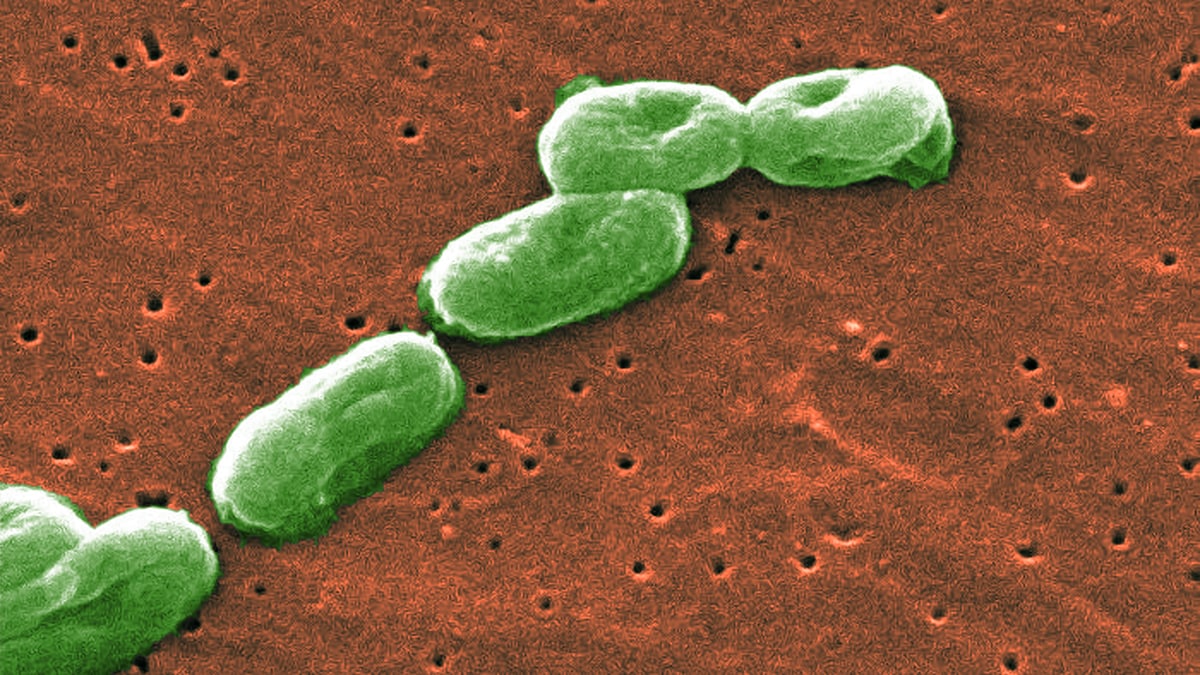
What it is
Burkholderia cepacia complex (Bcc) is a group of bacteria commonly found in soil and water.
Symptoms
Symptoms vary, ranging from no symptoms to serious respiratory infections, especially in patients with cystic fibrosis or other chronic lung disease. Other symptoms may include:
- Fever
- Fatigue
At-risk populations
In the United States, people in healthcare settings and those with weakened immune systems or chronic lung diseases, particularly cystic fibrosis, are at highest risk of infection with B. cepacia complex.
B. cepacia complex poses little medical risk to healthy people.
How it spreads
- Exposure from water, soil or aqueous (watery) environments.
- Contact with contaminated surfaces.
- Contact with contaminated equipment.
- Person-to-person transmission, more commonly in patients with cystic fibrosis.
Reducing risk
Patients and caregivers should:
- Keep their hands clean, particularly before and after caring for wounds or touching a medical device.
- Ask others to clean their hands before touching the patient or handling medical devices.
- Avoid exposing wounds and indwelling medical devices (devices put in or connected to the patient's body) to nonsterile water.
- Allow healthcare staff to clean their room daily when in a healthcare setting.
Healthcare providers should always follow recommended infection control practices to reduce the risk of spreading these germs to patients.
Treatment
Treatment decisions should be made on a case-by-case basis but generally include antibiotics. Unfortunately, many B. cepacia complex germs are resistant to antibiotics, which makes them difficult to treat.
Previous outbreaks
- Outbreak of Burkholderia stabilis Infections Associated with Contaminated Nonsterile, Multiuse Ultrasound Gel — 10 States, May–September 2021 | MMWR (cdc.gov)
- Multistate Outbreak of Burkholderia cepacia Infections Associated with Oral Liquid Docusate Sodium
- Multistate Outbreak of Burkholderia cepacia Bloodstream Infections Associated with Contaminated Prefilled Saline Flush Syringes
What CDC is doing
- Working closely with health departments, other federal agencies, healthcare providers and patients to prevent infections caused by B. cepacia complex.
- Tracking B. cepacia complex infections through the National Healthcare Safety Network.
