What to know
Since 1961, the American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended a single shot of vitamin K be given at birth. The shot protects against bleeding related to low levels of this essential vitamin. If you have concerns about vitamin K, please talk to your healthcare provider.
Q: What is vitamin K, and how do low levels of vitamin K and vitamin K deficiency bleeding occur in babies?
A: Vitamin K is used by the body to form clots and to stop bleeding. Babies are born with very little vitamin K stored in their bodies. This is called "vitamin K deficiency" and means that a baby has low levels of vitamin K. Without enough vitamin K, babies cannot make the substances used to form clots, called 'clotting factors.' When bleeding happens because of low levels of vitamin K, this is called vitamin K deficiency bleeding, or VKDB. VKDB is a serious and potentially life-threatening cause of bleeding in infants up to 6 months of age. A vitamin K shot given at birth is the best way to prevent low levels of vitamin K and VKDB.
Q: Why do ALL babies need a vitamin K shot—can't I just wait to see if my baby needs it?
A: No, waiting to see if your baby needs a vitamin K shot may be too late. Babies can bleed into their intestines or brain where parents can't see the bleeding to know that something is wrong. This can delay medical care and lead to serious and life-threatening consequences. All babies are born with very low levels of vitamin K, because unlike many other nutrients, vitamin K doesn't cross the placenta easily. Additionally, breast milk contains only small amounts of vitamin K.
That means that ALL newborns have low levels of vitamin K, so they need vitamin K from another source. A single vitamin K shot is the best way to make sure all babies have enough vitamin K. Newborns who do not get a vitamin K shot are 81 times more likely to develop severe bleeding than those who do get the shot.
Q: Doesn't the risk of bleeding from low levels of vitamin K only last a few weeks?
A: No, VKDB can happen to otherwise healthy babies up to 6 months of age. The risk isn't limited to just the first 7 or 8 days of life, and VKDB doesn't just happen to babies who have difficult births. VKDB has been reported in infants who were over 6 weeks old who had been healthy and developing normally. These infants had not received a vitamin K shot at birth.
Q: Isn't VKDB really rare?
A: VKDB is rare in the United States, but only because most newborns get the vitamin K shot. Over the past two decades, many countries in Europe have started programs to provide vitamin K at birth—afterward, they all saw declines in the number of cases of VKDB to very low levels. However, in areas of the world where the vitamin K shot isn't available, VKDB is more common, and many cases of VKDB have been reported from these countries.
In the early 1980s in England, some hospitals stopped giving vitamin K to all newborns; instead, they only gave it to those who were thought to be at higher risk for bleeding. These hospitals then noticed an increase in cases of VKDB. This tells us that giving vitamin K to prevent bleeding is what keeps VKDB a rare condition—when vitamin K is not given to newborns, cases of bleeding occur and VKDB stops being rare.
Q: What happens when babies have low levels of vitamin K and get VKDB?
A: Babies without enough vitamin K cannot form clots to stop bleeding and they can bleed anywhere in their bodies. The bleeding can happen in their brains or other important organs and can happen quickly. Even though bleeding from low levels of vitamin K or VKDB does not occur often in the United States, it is devastating when it does occur. One out of every five babies with VKDB dies. Of the infants who have late VKDB, about half of them have bleeding into their brains, which can lead to permanent brain damage. Others bleed in their stomach or intestines, or in other parts of the body. Many of the infants need blood transfusions, and some need surgeries.
Q: I heard that the vitamin K shot might cause cancer. Is this true?
A: No. In 1990, a small study in England found an "association" between the vitamin K shot and childhood cancer. An association means that two things are happening at the same time in the same person, but doesn't tell us whether one causes the other. Figuring out whether vitamin K might cause childhood cancer was very important because every newborn is expected to get a vitamin K shot. If vitamin K was causing cancer, we would expect to see the same association in other groups of children. Scientists have conducted multiple larger studies to see if they could find the same association in other children, but they have found no evidence supporting the link between vitamin K and childhood cancer.
Q: Can the other ingredients in the shot cause problems for my baby? Do we really know that the vitamin K shot is safe?
A: The vitamin K shot is safe. Vitamin K is the main ingredient in the shot. The other ingredients make the vitamin K safe to give as a shot. One ingredient keeps the vitamin K mixed in the liquid; another keeps the liquid from being too acidic. One of the ingredients is benzyl alcohol, a preservative. Benzyl alcohol is a common ingredient in many medications.
In the 1980s, doctors recognized that very premature infants who were in neonatal intensive care units might become sick from benzyl alcohol toxicity because many of the medicines and fluids needed for their intensive care contained benzyl alcohol as a preservative. Although the toxicity was only reported for very premature infants, since then doctors have tried to minimize the number of benzyl-alcohol-containing medications they give. Clearly, the small amount of benzyl alcohol in the vitamin K shot is not enough to be dangerous, even when given in combination with other medications that also contain small amounts of this preservative.
Q: The dose of the shot seems high. Is that too much for my baby?
A: No, the dose in the vitamin K shot is not too much for babies. The dose of vitamin K in the shot is high compared with the daily requirement of vitamin K. But remember, babies don't have much vitamin K when they are born and won't have a good supply of vitamin K until they are close to 6 months old. This is because unlike many other nutrients, vitamin K does not cross the placenta easily. Also, breast milk has very low levels of vitamin K.
The vitamin K shot acts in two ways to increase the vitamin K levels. First, part of the vitamin K goes into the infant's bloodstream immediately and increases the amount of vitamin K in the blood. This provides enough vitamin K so that the infant's levels don't drop dangerously low in the first few days of life. Much of this vitamin K gets stored in the liver and it is used by the clotting system. Second, the rest of the vitamin K is released slowly over the next 2–3 months, providing a steady source of vitamin K until an infant has another source from their diet.
Q: Can I increase vitamin K in my breast milk by eating different foods or taking multivitamins or vitamin K supplements?
A: We encourage moms to eat healthy and take multivitamins as needed. Although eating foods high in vitamin K or taking vitamin K supplements can slightly increase the levels of vitamin K in your breast milk, neither can increase levels in breast milk enough to provide all of the vitamin K an infant needs.
When infants are born, their already low levels of vitamin K fall even lower. Infants need enough vitamin K to (a) make up for their extra-low levels, (b) start storing it in the liver for future use, and (c) ensure good bone and blood health. Breast milk—even from mothers supplementing with vitamin K sources—can't provide enough to do all of these things.
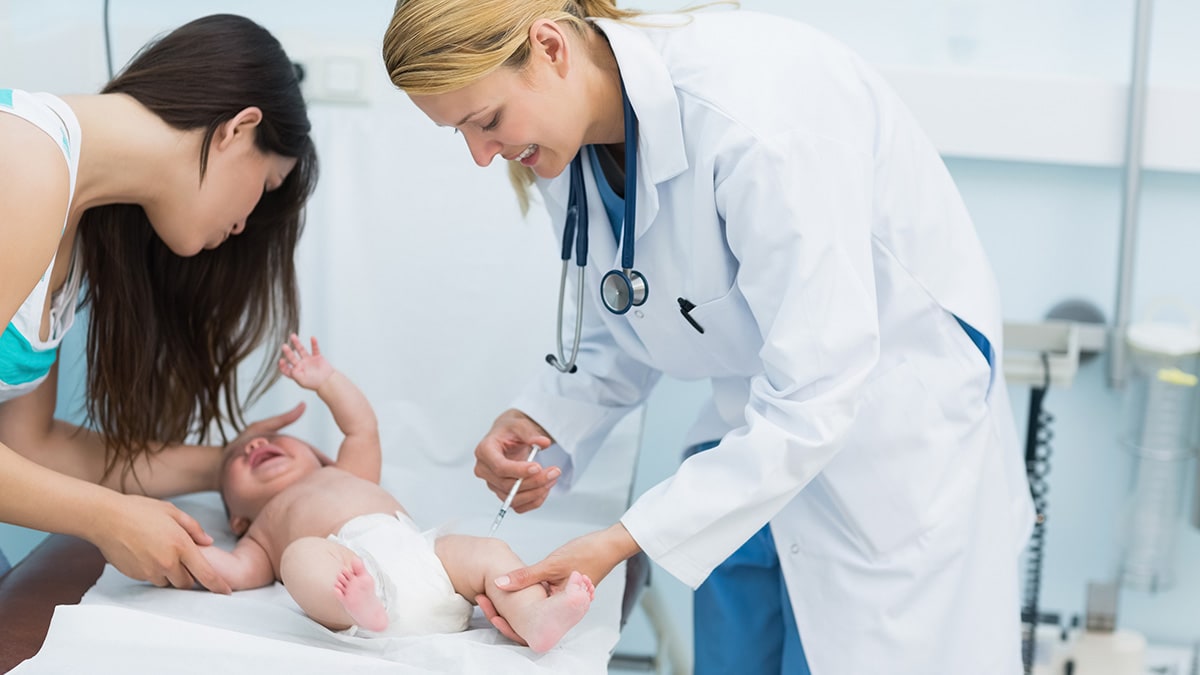
Q: My baby is so little. What can I do to make the vitamin K shot less painful and traumatic?
A: Babies, just like us, feel pain, and it is important to reduce even small amounts of discomfort. Babies feel less pain from shots if they are held and allowed to suck. You can ask to hold your baby while the vitamin K shot is given so that your baby can be comforted by you. Breastfeeding while the shot is given and immediately after can be comforting too. All of these are things parents can do to ease pain and soothe their baby.
Remember that if your baby does not get the vitamin K shot, their risk of developing severe bleeding is 81 times higher than if he or she got the shot. Diagnosis and treatment of VKDB often involves many painful procedures, including repeated blood draws.
Q: Overall, what are the risks and benefits of the vitamin K shot?
The risks of the vitamin K shot are the same risks that are part of getting most any other shot. These include pain or even bruising or swelling at the place where the shot is given. A few cases of skin scarring at the site of injection have been reported. Only a single case of allergic reaction in an infant has been reported, so this is extremely rare.
The main benefit of the vitamin K shot is that it can protect your baby from VKDB, a dangerous condition that can cause long-term disability or death. In addition, the diagnosis and treatment of VKDB often includes multiple and sometimes painful procedures, such as blood draws, CT scans, blood transfusions, or anesthesia and surgery.
The American Academy of Pediatrics has recommended the vitamin K shot since 1961—and has repeatedly stood by that recommendation because the risks of the shot don't outweigh the risks of VKDB, which are based on decades of evidence and decades of experience with babies who were hospitalized or died from VKDB.
Your child's doctor is the best person to talk to about vitamin K. Like you, your child's doctor wants to see them grow up safe and healthy and wants to support your efforts to make the best decisions for their health. If you have concerns about vitamin K, talk to your child's doctor.
