At a glance
The Enhancing Data-driven Disease Detection in Newborns (ED3N) pilot program aims to provide a national data platform that will improve the quality and interpretation of newborn screening results.

Overview
Newborn screening (NBS) professionals in the U.S. face greater data analytic challenges because of the continued expansion in the number of diseases being screened for by NBS programs. Other challenges include increased difficulty in disease detection and matching disease markers with risk and severity.
The addition of late-onset diseases to newborn screening panels requires a process to routinely capture clinical data and outcomes.
The Enhancing Data-driven Disease Detection in Newborns (ED3N) pilot program will assess the functionality of a CDC data platform in the Division of Laboratory Sciences Newborn Screening and Molecular Biology Brance (NSMBB). The project aims to help improve disease detection in newborns through dried blood spot screening.
Through collaboration between U.S. newborn screening programs and CDC's Newborn Screening and Molecular Biology Branch, the ED3N pilot project will help programs evaluate disease risks. The NSMBB project will pilot two modules within ED3N.
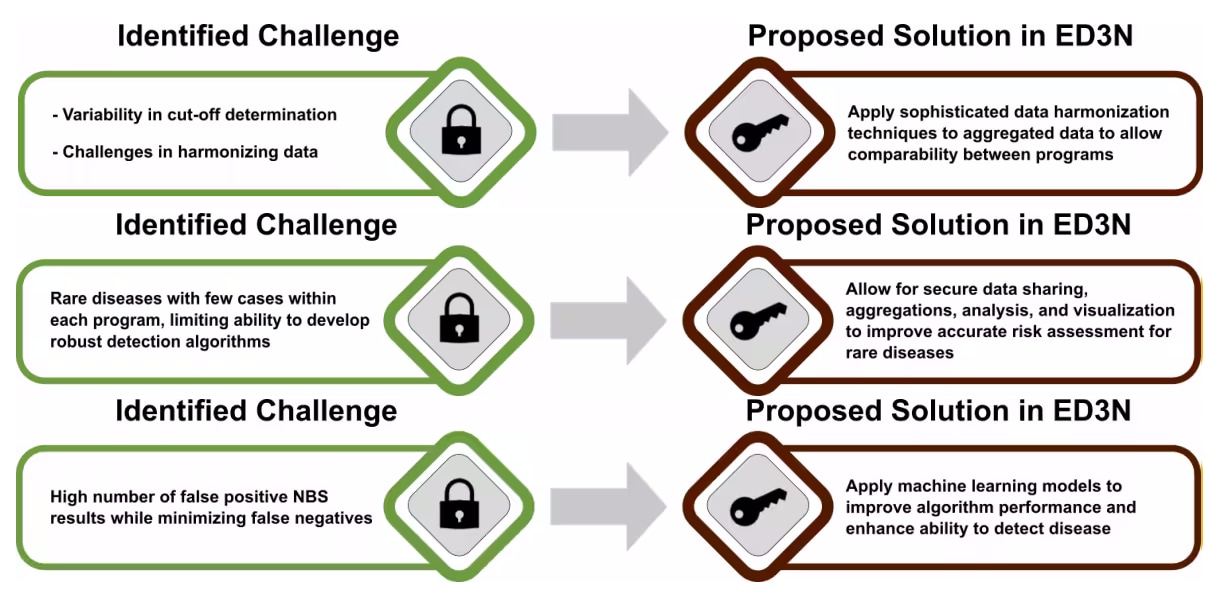
Biochemical analysis
Biochemical testing of analyte markers in dried blood spots is the traditional core of the newborn screening process. It faces ongoing challenges as the testing panel and complexity of diseases continue to grow.
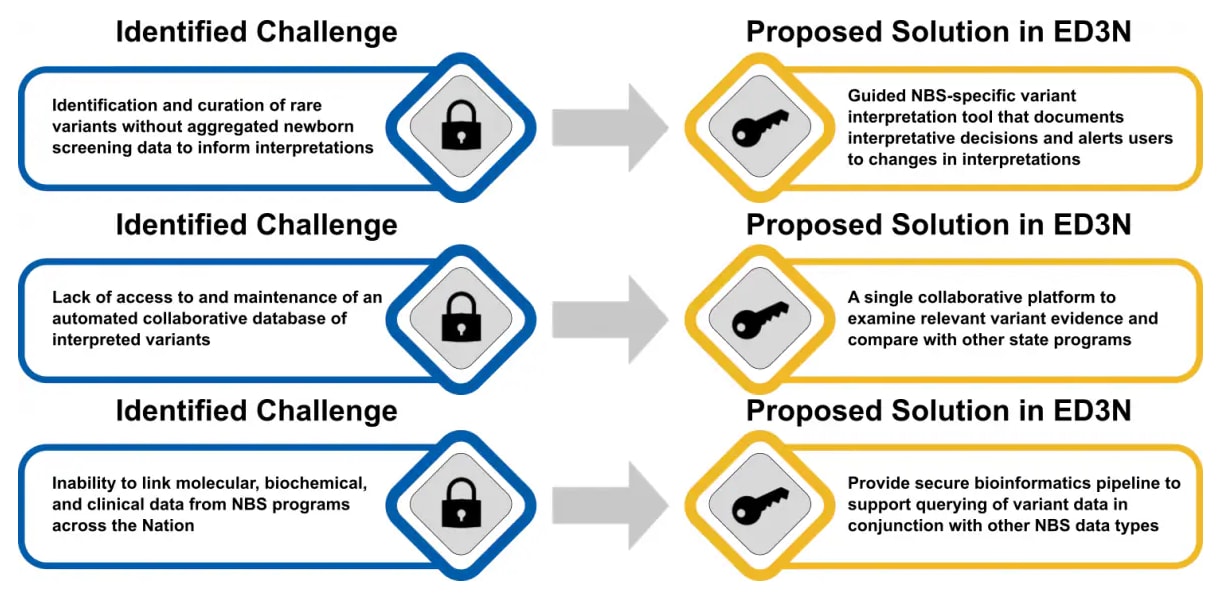
Molecular analysis
Molecular testing has traditionally been used in newborn screening as a second or third-tier test after out-of-range biochemical testing results. The purpose of molecular testing in newborn screening is often to improve sensitivity and specificity and allow for the differentiation of disease onset and/or severity.