Key points
- Most people get HIV through anal or vaginal sex, or sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment.
- Only certain body fluids can transmit HIV.
- There are powerful tools to help prevent HIV transmission.
Body fluids that transmit HIV
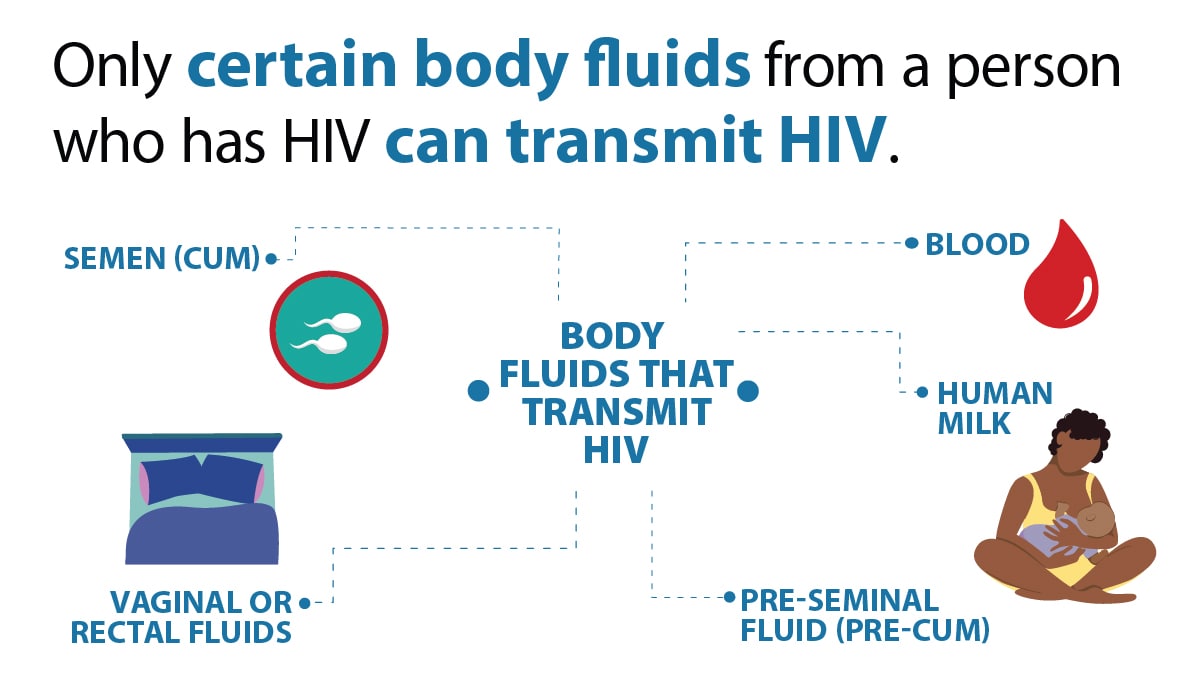
These fluids must come into contact with a mucous membrane or damaged tissue or be directly injected into the bloodstream (from a needle or syringe) for transmission to occur. There are mucous membranes inside the rectum, vagina, penis, and mouth.
How HIV is transmitted
You can get HIV if you have anal or vaginal sex with someone who has HIV without using protection (like condoms or medicine to prevent HIV). You can also get HIV from sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment (for example, cookers) with someone who has HIV. Pregnant people can pass HIV to their baby during pregnancy, childbirth, and breast/chestfeeding.
Chance of getting HIV per sex act
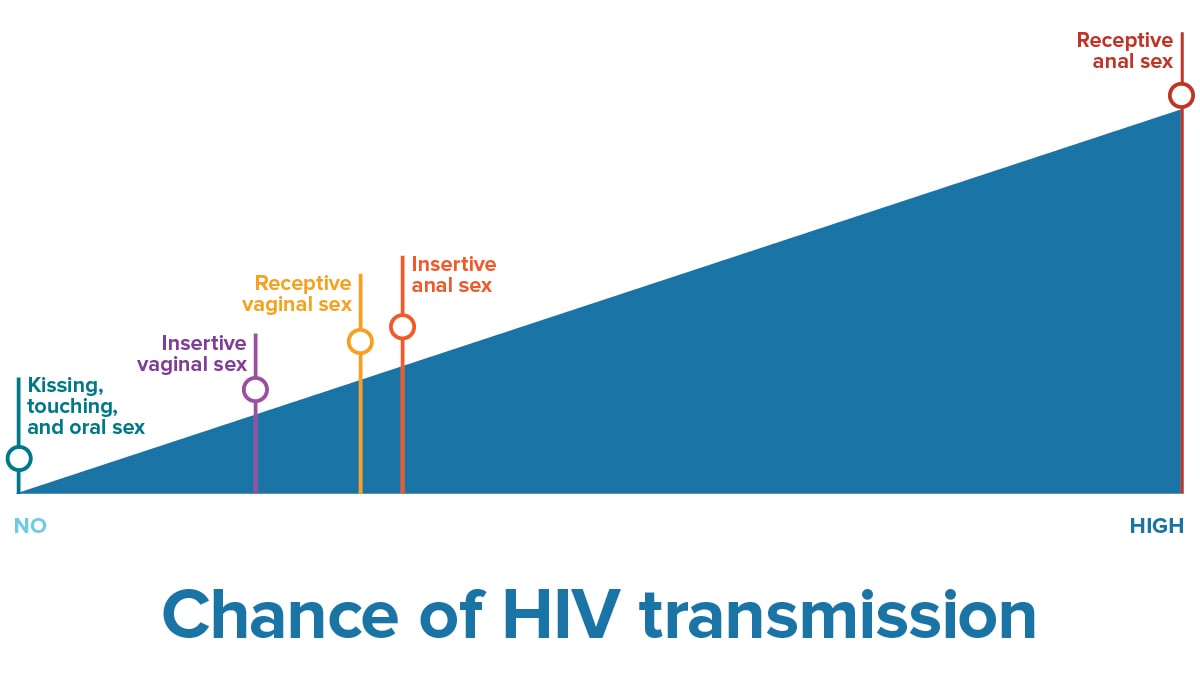
Visit CDC's HIV Risk Reduction Tool to learn more about the chance of getting HIV from different sex activities.
Anal sex
- Either partner can get HIV during anal sex.
- Being the bottom or having your partner's penis inside your rectum (butthole) makes you more likely to get HIV than being the top or putting your penis inside your partner's rectum.
- HIV can enter the body through the lining of the rectum (butthole), the opening at the tip of the penis (urethra), the foreskin, or cuts or sores on the penis.
Vaginal sex
- Either partner can get HIV during vaginal sex.
- HIV can enter a person's body through the tissue that lines the vagina and cervix.
- Vaginal fluid and blood can pass through the opening at the tip of the penis (urethra), the foreskin, or cuts or sores.
Injection drug use
- Used needles, syringes, and other injection equipment may have someone else's blood in them.
- People who inject drugs may be more likely to engage in sexual behaviors that increase their chances of getting HIV.
Perinatal transmission
- HIV can pass to a baby during pregnancy, childbirth, and breast/chestfeeding. This is called perinatal transmission.
- This is the most common way that children get HIV.
Did you know?
You can't get or transmit HIV from activities that don't involve contact with body fluids (e.g., touching). HIV does not survive long outside the human body (for example, on surfaces) and cannot reproduce outside a human host.

Risk factors
Viral load
Viral load is the amount of HIV in the blood of someone who has HIV. The higher someone's viral load, the more likely that person is to transmit HIV. Viral load is highest during the acute phase of HIV, and without HIV treatment.
Learn more about how taking HIV treatment and having an undetectable viral load prevents HIV transmission through sex or sharing needles, syringes, or other injection equipment, and from a pregnant person to their child during pregnancy, birth, and breast/chestfeeding.
Other sexually transmitted infections
If you have another sexually transmitted infection (STI), you may be more likely to get or transmit HIV. Getting tested and treated for STIs can lower your chances of getting or transmitting HIV and other STIs. If you're sexually active, you and your partner(s) should get tested for STIs, even if you don't have symptoms.
Alcohol and other drug use
When you use drugs, you may be more likely to engage in behaviors that increase your chances of getting or transmitting HIV such as:
- Having anal or vaginal sex without protection (like a condom or medicine to prevent HIV)
- Sharing needles, syringes, or other drug injection equipment—for example, cookers
- Having sex with multiple partners
- Trading sex for money or drugs
Using drugs or drinking alcohol can alter your judgment, lower your inhibitions, and impair your decisions about sex or drug use.
If you're going somewhere you know you'll be drinking or using drugs, bring a condom to reduce your chances of getting or transmitting HIV through sex.
Extremely rare ways HIV might be transmitted
There is little to no risk of getting HIV from the activities below. For transmission to occur, something very unusual would have to happen.
Oral sex
Oral sex involves putting the mouth on the penis (fellatio), vagina or vulva (cunnilingus), or anus (rimming). Ejaculation in the mouth with oral ulcers, bleeding gums, or genital sores or the presence of other STIs) can increase the chances of HIV transmission. You can get other STIs from oral sex.
Workplace
The most likely cause is injury with a contaminated needle or another sharp object. Careful practice of standard precautions protects patients and health care personnel from possible occupational HIV transmission.
Medical care
The US blood supply and donated organs and tissues are thoroughly tested. It is very unlikely that you would get HIV from blood donation or transfusion, blood products, or organ and tissue transplants. You cannot get HIV from donating blood. Blood collection procedures are highly regulated and safe.
Food
The only known cases of HIV transmission through food have been when blood from a caregiver’s mouth mixed with pre-chewed food and an infant has eaten it. You cannot get HIV from consuming food handled by someone with HIV.
Biting
This rare transmission has only occurred through contact between broken skin, wounds, or mucous membranes and blood or body fluids from a person who has HIV. The small number of documented cases have involved severe bite trauma with extensive tissue damage and the presence of blood.
There is no chance of transmission if skin is unbroken or through spitting. HIV is not transmitted through saliva.
Deep, open-mouth kissing
Very rarely, transmission has occurred if both partners had sores or bleeding gums. You cannot transmit HIV through closed-mouth kissing. You cannot transmit HIV through saliva alone.
Tattoos, body piercings, and cosmetic procedures
The only known cases of HIV transmission through cosmetic procedures have been from unsafe infection control procedures involving injections. Although there are no known cases of anyone getting HIV from tattoos or body piercings, it is possible to get HIV this way if the equipment or ink contains blood from someone with HIV. Be sure the tattoo, piercing, or cosmetic procedure facility is properly licensed and uses only new or sterilized equipment.
