At a glance
CDC established an office in Zimbabwe in 2000. CDC works with Zimbabwe's Ministry of Health and Child Care (MOHCC) and local organizations to support health systems strengthening and increase access to quality HIV and malaria interventions.

Overview
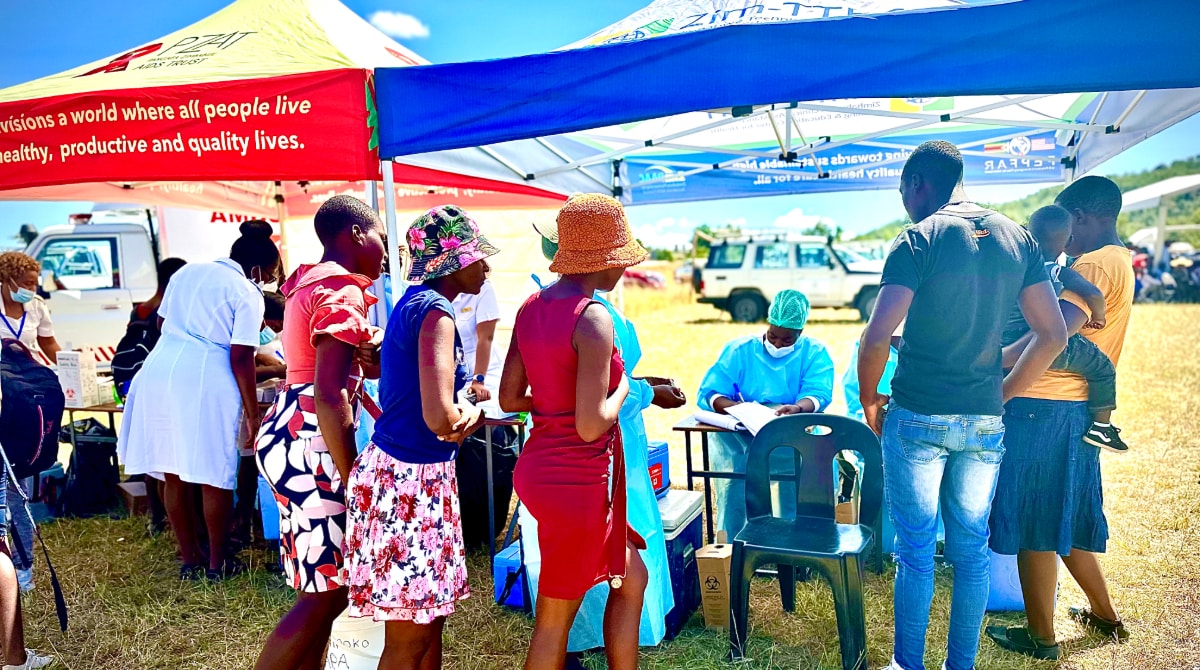

CDC Zimbabwe works to address the following public health areas:
- HIV prevention, care, and treatment
- Tuberculosis (TB)
- Cervical cancer
- Extramural management
Global health security
Strategic focus
CDC's global health security work in Zimbabwe focuses on strengthening the country's public health systems across the following core areas:
Laboratory systems strengthening
CDC Zimbabwe has provided support to the MOHCC laboratory services since 2004. CDC has also provided technical assistance to laboratories across the country to attain ISO 15189 accreditation for quality diagnostic services.
Key achievements
- Supported accreditation of 15 public health laboratories, including the national microbiology reference lab and the national TB reference labs.
- Optimized national integrated sample transport systems coverage and access with 720,930 samples transported to 15 viral load testing laboratories from health facilities in 44 districts, providing HIV, TB, and other disease diagnostics services.
Surveillance and health information systems
CDC Zimbabwe supported the MOHCC's strategic information activities. Activities included providing technical leadership and programmatic guidance for:
- Routine program monitoring, implementing, and using case-based and recency surveillance data to inform program planning.
- Health management information system support, including supporting the development and implementation of an electronic health record (EMR) systems and transition of patient registers from paper-based to the electronic health system.
- Implementing population based and Biobehavioral Surveys (BBS) to measure progress towards achieving HIV epidemic control and inform HIV program planning.
Key achievements
- Through a partnership with ICAP at Columbia University, CDC conducted the first BBS among men who have sex with men (MSM) and transgender women/gender queer people (TGW/GQ) in 2019.
- CDC will conduct another BBS survey among MSM, TGW, and people who inject drugs in 2024.
- CDC will conduct another BBS survey among MSM, TGW, and people who inject drugs in 2024.
- Expanded use of the EMR system in health facilities in Zimbabwe.
Emergency response
CDC Zimbabwe and partners continue to support the MOHCC to prevent, respond to, and strengthen health systems to address public health threats like COVID-19. Through CARES ACT funding, the U.S. government supported COVID-19 infection prevention and control (IPC) activities. This included harmonization and strengthening of IPC measures in 105 health care facilities to build sustainable health systems and preparedness for any future pandemics.
CDC has also provided technical support for other outbreaks such as cholera, polio, and measles. CDC is currently providing technical assistance to strengthen national capacities on quality monitoring for water, sanitation, and hygiene and cholera preparedness and response.
HIV and TB
Strategic focus
With support from the President's Emergency Plan for AIDS Relief (PEPFAR), CDC and the MOHCC work to build a robust national HIV and TB response. CDC Zimbabwe efforts include:
- Addressing acute staff shortage in the public health sector through investments in health workforce support.
- Scaling up HIV prevention, including increasing delivery of differentiated HIV diagnostic services, oral pre-exposure prophylaxis and new prevention technologies, and voluntary medical male circumcision.
- Focusing outreach on the most at risk and vulnerable groups, including training girls on sexual violence prevention and supporting employment for young women through the Determined, Resilient, Empowered, AIDS-free, Mentored, and Safe program.
- Enhancing HIV care and treatment by increasing the number of people living with HIV (PLHIV) on antiretroviral therapy (ART), scaling up comprehensive outreach services, transitioning clients to optimized ART regimens including the dolutegravir-based regimens, and scaling-up targeted interventions for preventing mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
- Scaling up TB programming to increase the number of PLHIV who have completed TB Preventive Therapy (TPT) and to optimize TB screening and diagnosis using LF-LAM and GENE-Xpert.
HIV and cervical cancer
Many women are surviving HIV but dying from cervical cancer. CDC Zimbabwe supported the MOHCC with screening women older than 25 years for cervical cancer and treating those with pre-cancerous lesions using LEEP.
Key achievements
- Over 579,000 PLHIV were provided with HIV treatment and maintained on ART.
- Over 95% of newly identified PLHIV were linked to treatment services in 2022.
- Over 95% of newly identified PLHIV were linked to treatment services in 2022.
- Considerable progress has been realized towards achieving the UNAIDS 90-90-90 targets with 87%, 97%, and 90% achievement.
- Over half a million PLHIV at high risk of developing TB completed TPT from around 2019 to 2023.
- Over 102,000 women living with HIV were screened for cervical cancer, 5,885 screened positive for pre-cancerous lesions and 78% were treated by the end of the 2023 reporting period, leading to decreased morbidity and mortality from cervical cancer disease.
Extramural management
Strategic focus
CDC Zimbabwe has continued the transition of complex and critical portfolios from international organizations to local organizations. CDC's focus is on continuing to enhance the capacity of local partners to manage cooperative agreements. CDC provides guidance and resources for the implementation, administration, oversight of awards, and managing accountability efforts.